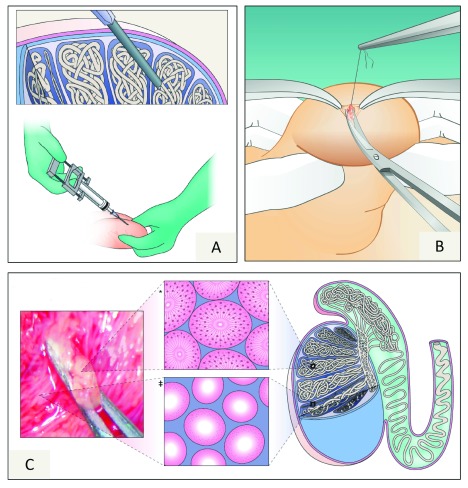
Figure 2. Sperm retrieval methods.
( A) Testicular sperm aspiration. The illustration depicts a 13G needle—connected to a 20-mL syringe and fitted to the Cameco holder—being percutaneously inserted into the testis. Negative pressure is created, and the tip of the needle is moved within the testis to disrupt the seminiferous tubules and sample different areas. ( B) Testicular sperm extraction (TESE). Single or multiple incisions are made on the tunica albuginea, and one or several testicular biopsies are taken. ( C) Microsurgical TESE (micro-TESE). With aid of an operating microscope, the dilated seminiferous tubules are identified and removed with microforceps. The illustration in the middle of the figure depicts histopathology cross-sections of dilated seminiferous tubules with active spermatogenesis* and a thin tubules with germ cell aplasia ‡. Adapted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd 3.