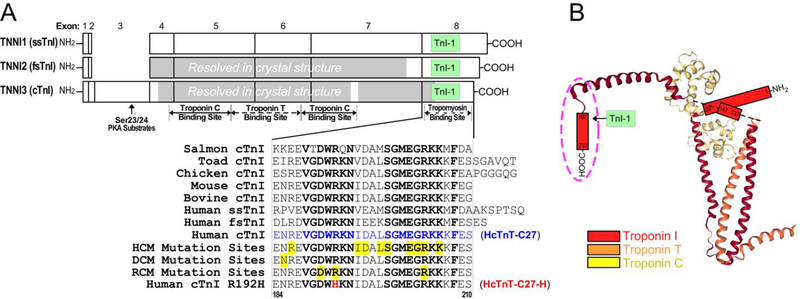
Figure 1: The highly conserved C-terminal end segment of TnI.
(A) Linear structures of the three isoforms of human TnI are aligned to show their exon organizations, major functional sites and the location of the mAb TnI-1 epitope. The regions resolved in the crystal structure of human cardiac troponin and chicken fast skeletal muscle troponin are shaded. The highly conserved amino acid sequences of the exon 8-encoded C-terminal end segment of cardiac (cTnI), slow skeletal muscle (ssTnI) and fast skeletal muscle (fsTnI) isoforms from representative vertebrate species are shown by the alignment. The conserved residues are bolded and known cardiomyopathic mutation sites are highlighted in yellow, among which the RCM mutation R192H is shown in red. (B) The crystal structure of cardiac troponin complex is depicted (PDB ID: 1J1E) to illustrate the position of TnI C-terminal end segment (in the dash oval) among the unresolved regions.