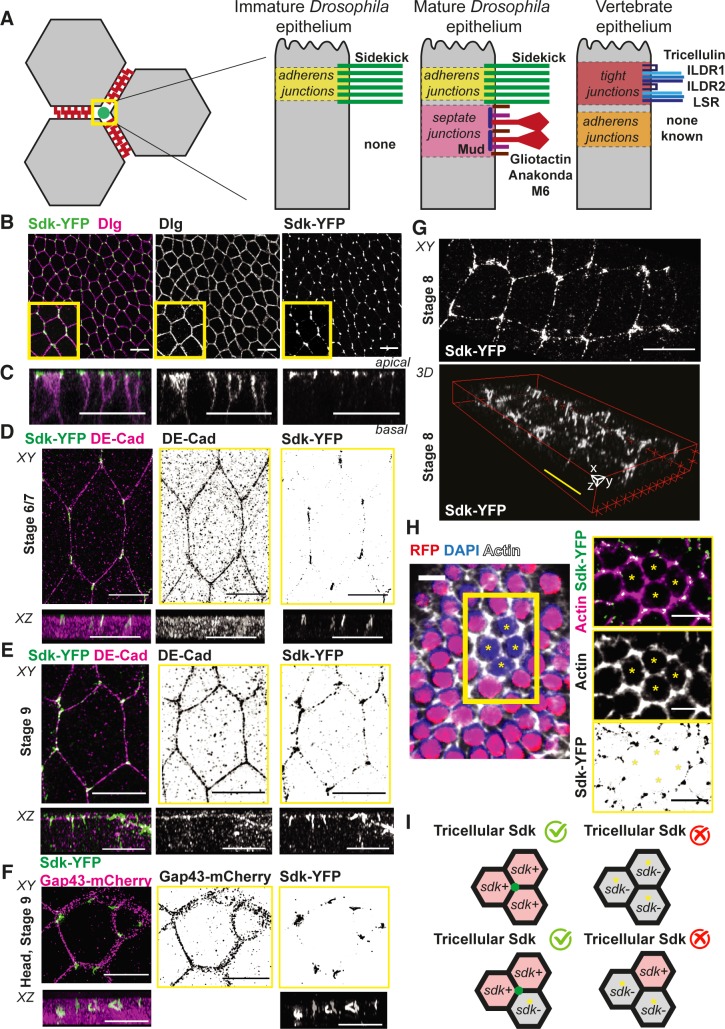
Fig 1. Sdk is a novel component of apical vertices in epithelia.
(A) Cartoon summarising the geometry of tricellular vertices and the proteins known to localise specifically there in epithelia of different types. (B,C) Immunostaining of fixed ventral ectoderm of stage 7 Drosophila embryos for Sdk-YFP and the lateral marker Dlg. (B) Maximum projection. Scale bar = 5 μm. (C) Z-reconstruction based on confocal slices taken from confocal stack in B. Scale bar = 20 μm. (D–G) Super-resolution SIM imaging of fixed embryos immunostained with Sdk-YFP and either DE-Cad to show the position of AJs (D,E) or Gap43-mCherry (F) to label the whole membrane. This reveals the localisation of Sdk in ‘strings’ at apical vertices in embryonic epithelia. Images are maximum projection (labelled XY) and z-reconstruction (labelled XZ) from z-slices of the apical side of the cells. Scale bars, apical views (top panels) = 5 μm; lateral views (bottom panels) = 2 μm. (G) 3D reconstruction to show the z-component of the strings. Scale bars = 5 μm. (H) Example of an sdkΔ15 clone (absence of nls-RFP signal) in the follicular epithelium (stage 6 egg chamber) stained for Sdk-YFP and actin phalloidin. Right panels show a close-up of the four-cell clone (asterisks) with individual channels on the left to show Sdk-YFP and actin, respectively, and the merge. Scale bars = 20 μm. (I) Cartoon summarising the results of the clone experiment shown in H. Vertex localisation of Sdk requires Sdk proteins in at least two of the three cells forming a vertex. AJ, adherens junction; DE-Cad, DE-cadherin; Dlg, Discs large; Gap43, growth-associated protein 43; ILDR, Immunoglubulin-like domain-containing receptor; LSR, Lipolysis-stimulated lipoprotein receptor; nls, nuclear localisation signal; RFP, red fluorescent protein; Sdk, Sidekick; SIM, Structured Illumination Microscopy; YFP, yellow fluorescent protein.