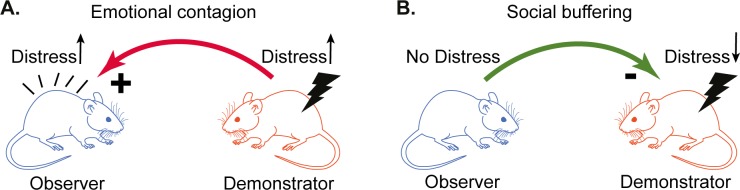
Fig 1. Emotional contagion and social buffering paradigms.
(A) A schematic representation of typical paradigms used to investigate emotional contagion. An observer rat witnesses a demonstrator rat receive an electric foot shock. The shock induces fear and pain responses in the demonstrator, which in turn is unidirectionally transferred to the observer, which shows increased freezing thought to indicate an increase in distress. In these paradigms, the variable of interest is the amount of freezing of the observer. (B) A schematic representation of the social buffering paradigm. A demonstrator rat receives an electric foot shock. The fear response of the demonstrator, freezing in particular, is reduced in the presence of an observer rat. The variable of interest is the amount of freezing of the demonstrator.