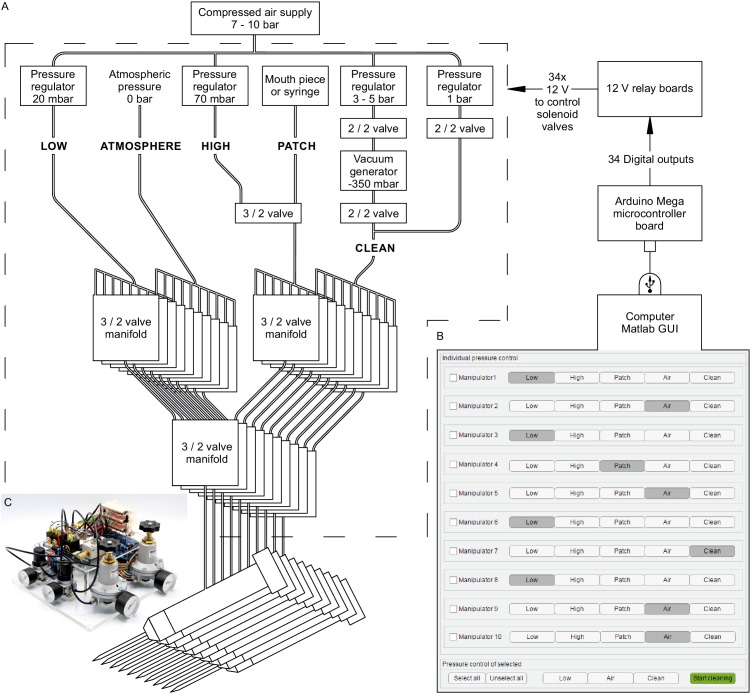
Figure 2. Automated pressure system.
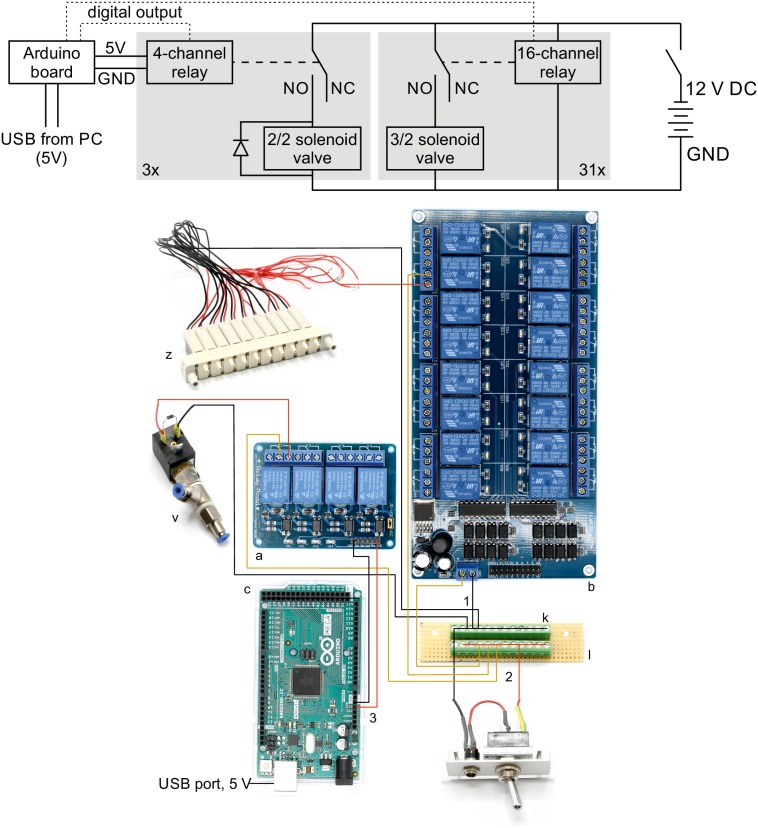
(A) Tubing scheme between the different pneumatic components. Top row depicts pressure regulators and their set pressure for each path. 2/2 valves are solenoid valves with two ports and two positions (open or closed). 3/2 valves are miniature solenoid valves with three ports and can switch between two positions connecting either inlet to one outlet. An illustrated step-by-step assembly guide of the pressure system can be found in Appendix 1. (B) Screenshot of Matlab GUI controlling the pressure system. It communicates with an Arduino microcontroller board which in turn has digital outputs connecting onto a relay board. For further details of wiring scheme see Figure 2—figure supplement 1. For more information on GUI see appendix 2. (C) Photograph of an assembled pressure system.