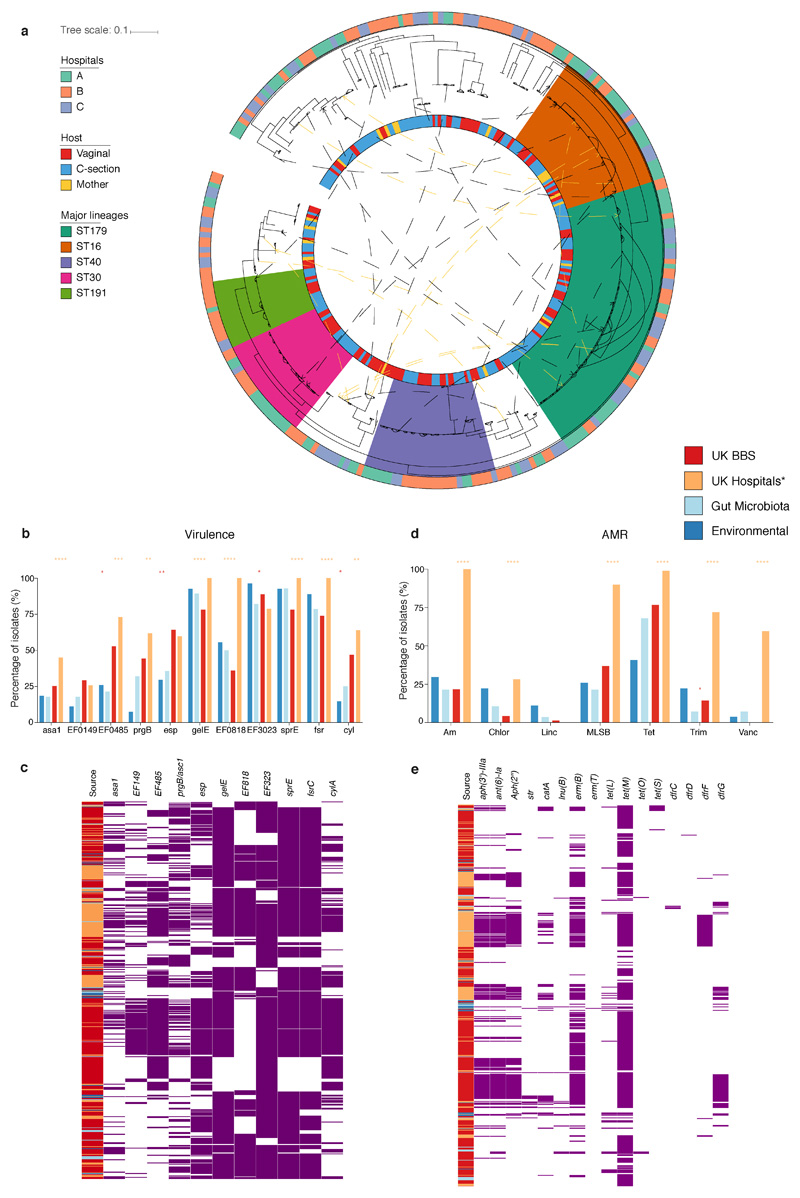
Extended Data Fig. 6. Phylogeny and pathogenicity potential of the BBS E. faecalis strains.
a, Phylogenetic tree of the BBS E. faecalis strains (n=282, isolated from 269 faecal samples of 160 subjects). Midpoint-rooted maximum likelihood is based on SNPs in 1,827 core genes. The five major lineages (>10 BBS strain representatives; ST179, n=60; ST16, n=30, ST40, n=27; ST30, n=21, ST191, n=14) identified with UK hospital collection distributed across three hospitals in this study with no phylogroup limited to any single hospital. Solid lines between indicated the intra-subject persistence (n=92 in 67 babies). Dash lines indicated phylogenetically distinct strains isolated from longitudinal samples (n=18) or mother-baby paired samples (yellow, n=10) with arrows indicating the direction of potential transmission (early-to-later or mother-to-baby). Where multiple identical strains (no SNP difference in species core-genome) were isolated from the same faecal sample, only one representative strain was included in the species phylogenetic tree (total number of strains, n=356). b-e, Prevalence of virulence (b-c) and AMR genes (grouped by antibiotic class) (d-e) were detected in the BBS E. faecalis strains. Statistical significance results shown are coloured according to the group with higher frequency of detected genes by two-sided Fisher's exact test between the groups of gut microbiotas (n=28) versus BBS strains (n=356), and BBS versus the UK hospital epidemic strains (n=89, tree branches coloured blue in Fig. 4c). ****P<0.0001, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05. Virulence genes: asa1, EF0149, EF0485, prgB = Aggregation substance; esp = enterococcal surface protein; Exoenzymes: gelE = gelatinase; EF0818, EF3023 = hyaluronidase (spreading factor); sprE = serine protease; fsr = Quorum sensing system; Toxin: cyl = cytolysin. Genes that detected across all isolates (dfrE, efrA, efrB, emeA, lsaA) are not shown. AMR genes: Am = aminoglycosides (aph3"-III, ant(6)-Ia, aph(2''), str); Chlor = chloramphenicol (catA); Linc = lincosamides (lnuB); MLSB = macrolide, lincosamide, streptogramin B (ermB or ermT); Tet = tetracycline (tetL, tetM, tetO, tetS); Trim = trimethoprim (dfrC, dfrD, dfrF or dfrG); Vanc = vancomycin.