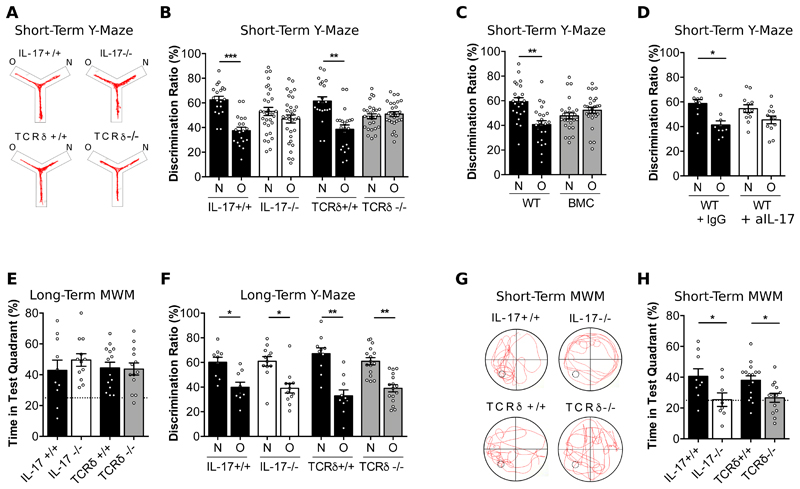
Figure 4. γδ T cells producing IL-17 are required for short-term memory.
(A) Representative track line from indicated animals exploring the short-term Y-maze. (B-D) Cognitive performance in the short-term Y-maze evaluated by discrimination ratio between the novel arm (N) versus the other arm (O) of IL-17-/-, TCRδ-/- compared to respective littermate controls (n=21-32) (B), WT → WT bone marrow chimeras (BMC) mice (n=23-27) (C) and WT after intra-cerebro-ventricular injection of isotype control (IgG) or anti-IL-17 (aIL-17) (n=10-12) (D). (E) Percentages of swimming time in the test quadrant of IL-17-/- and TCRδ-/- and respective littermate controls during the probe test of the long-term Morris Water Maze (MWM) (n=10-14). (F) Cognitive performance in the long-term Y-maze evaluated by discrimination ratio between the novel arm (N) versus the other arm (O) of IL-17-/-, TCRδ-/- compared to respective littermate controls (n=10-16). (G) Representative track line from indicated animals exploring the short-term Morris Water Maze (MWM) during the probe test, after a training phase with a platform in the lower left quadrant of the pool. (H) Corresponding percentages of time spent in the test quadrant of IL-17-/- and TCRδ-/- and respective littermate controls (n=8-16). Results are representative of 2-3 independent experiments in male mice. Error bars, mean + s.e.m. **P<0.05; **P<0.0; ***P<0.001. Paired Student’s t-test and One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test were used to analyse discrimination ratio (%) and Time in quadrant (%) respectively.