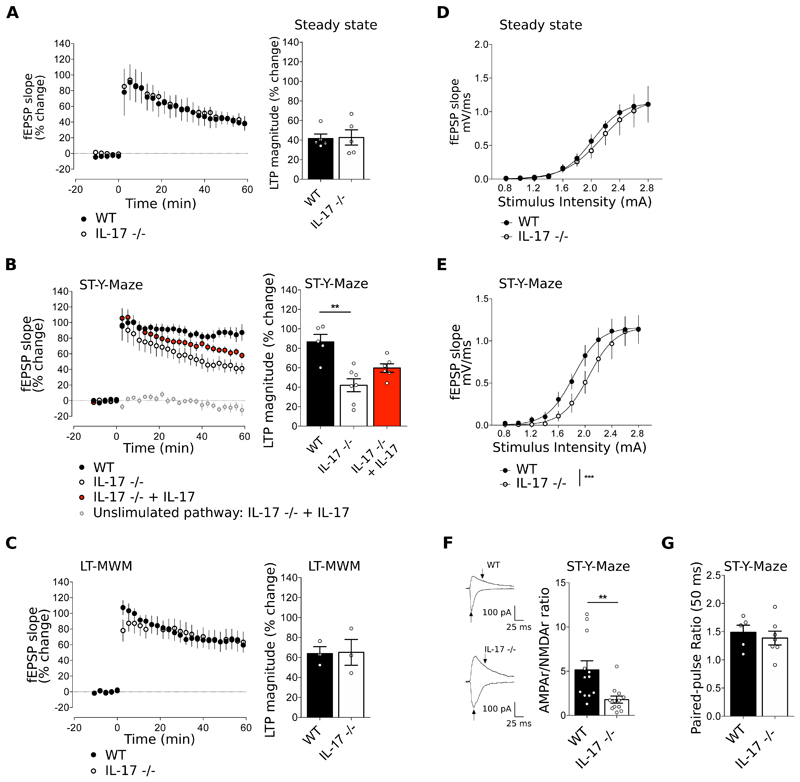
Figure 5. IL-17 modulates synaptic plasticity and AMPA/NMDA ratio upon a short-term memory task.
(A-C) Time course (left panels) and magnitude (right panels) of LTP induced by theta-burst stimulation (TBS) in hippocampal slices from WT and IL-17-/- mice at steady state (A), after training in the short-term Y-Maze (B) and after training in the long-term MWM (C). When indicated, hippocampal slices from IL-17-/- mice were supplemented with IL-17 (10ng/mL) (n=3-7, Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn's multiple comparisons test). (D-E) Input/Output (I/O) curves corresponding to the fEPSP slope evoked by different stimulation intensities (0.8-2.8 mA) of IL-17-/- compared to WT mice at steady state (D) and after training in the short-term Y-maze test (E) n=5-7, F-test. (F) Representative traces of EPSCs recorded at −70 mV and + 40 mV in neurons from WT and IL-17 -/- mice after training in the short-term Y-maze (left panels). Arrows indicate the amplitudes considered to calculate AMPAR/NMDAR ratio, depicted in the right panel. n=11-12, unpaired T-test. (G) Paired Pulse Facilitation, EPSCs at 50 ms interpulse intervals in WT and IL-17-/- after Y-maze (n=5-7, Mann-Whitney test). Data are mean ± s.e.m. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.