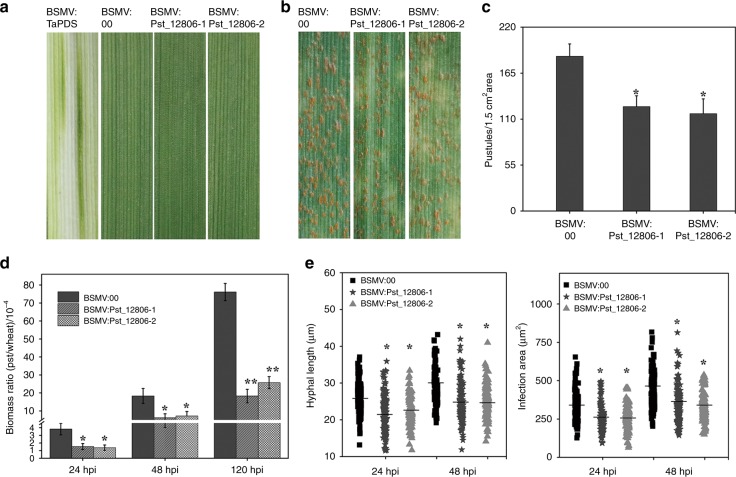
Fig. 4. Silencing Pst_12806 weakens the virulence of Pst.
a The second leaves of two-leaf stage wheat cultivar Suwon 11 were inoculated with barley stripe mosaic virus BSMV: 00 and recombinant BSMV:TaPDS, BSMV: Pst_12806-1, BSMV: Pst_12806-2, and the virus phenotypes were observed and photographed at 10 days after inoculation. b Seedlings of cultivar Suwon 11were inoculated with the labeled BSMV constructs on the second leaf for 10 days and then inoculated with urediniospores of Pst CYR31 on the fourth leaf. Leaves infected with Pst were examined at 14 dpi. c The number of uredinium pustules formed by Pst per 1.5 cm2 on the fourth leaves of wheat plants treated with the labeled BSMV were scored at 14 dpi. Mean and standard deviation were calculated with results from three independent replicates, with 15–20 leaves examines in each replicate. The asterisks indicate significant difference (P < 0.05). d The Pst/wheat biomass ratio was assayed by qRT-PCR with RNA isolated from the fourth leaves of the same set of wheat plants as Fig.4c at 24, 48, and 120 hpi as described66. TaEF-1α and PstEF-1α were used to normalize the RNA level of wheat leaves and Pst, respectively. Mean and standard deviations were calculated with data from three independent replicates. The asterisks indicate significant difference in samples with Pst_12806 silenced by HIGS in comparison with the control (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01). e The hyphal length and infection area of Pst on the fourth leaves of the same wheat samples of 4 days were analyzed with CellSens Entry software at 24 and 48 hpi. Means were calculated from 50 infection sites of three biological replicates and were represented as solid lines in the picture. An asterisk indicates significant differences (P < 0.05) using unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test.