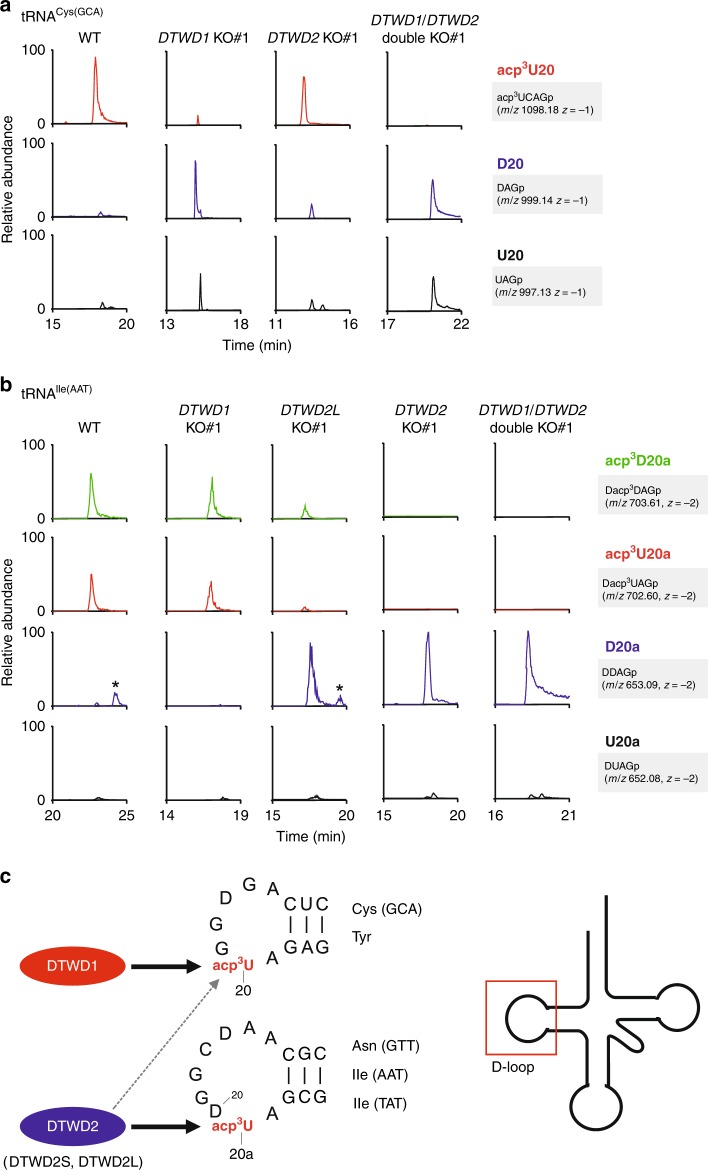
Fig. 4. Human DTWD1 and DTWD2 are responsible for acp3U formation.
a Mass spectrometric analyses of acp3U20 in tRNACys(GCA) isolated from WT (left), DTWD1 KO (left middle), DTWD2 KO (right middle), and DTWD1/DTWD2 double-KO (right) strains. XICs show corresponding negative ions of the RNase T1-digested fragments as indicated on the right-hand side of each chromatogram. Mass spectra of acp3D- or D-containing fragments overlap with the isotopic peaks of acp3U- or U-containing fragments. The peak intensities of these fragments are normalized in consideration of those isotopes. Asterisk indicates nonspecific peaks with the same m/z value. b Mass spectrometric analyses of acp3U20a in tRNAIle(AAT) isolated from WT (left), DTWD1 KO (left middle), DTWD2L KO (middle), DTWD2 KO (right middle), and DTWD1/DTWD2 double-KO (right) strains. c Substrate specificity of human DTWD1 and DTWD2. DTWD1 is responsible for acp3U20 formation in tRNAs for Cys(GCA) and Tyr, whereas DTWD2 is responsible for acp3U20a formation in tRNAs for Asn(GTT), Ile(AAT), and Ile(TAT). DTWD2 also has a weak activity to form acp3U20. The sequence of tRNACys and tRNAAsn are shown.