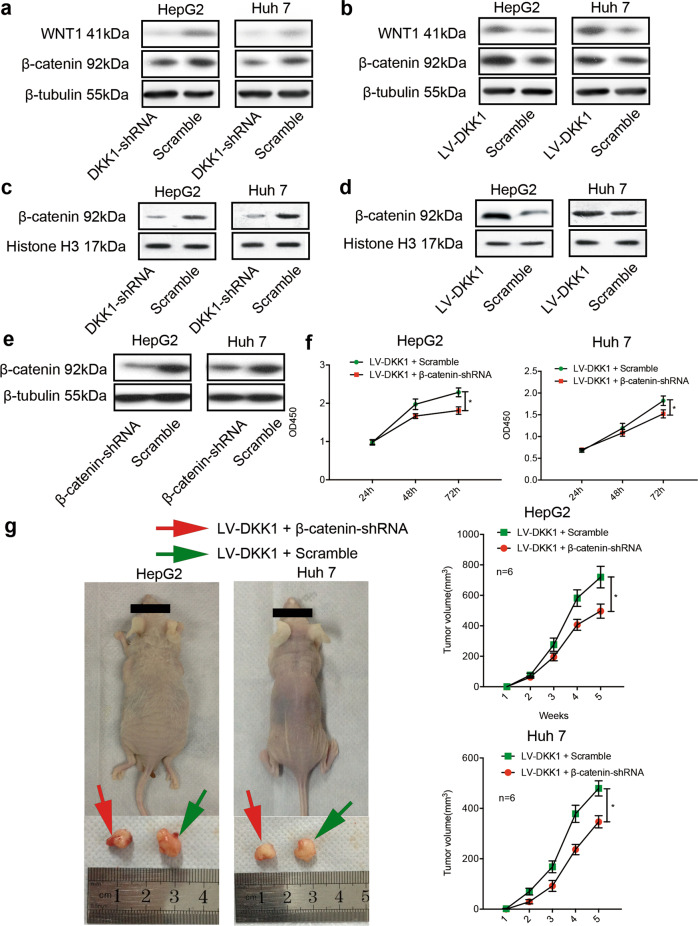
Fig. 6.
DKK1-mediated proliferation and tumor formation are dependent on the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in human HepG2 and HUH-7 cells. The protein levels of WNT1, β-catenin, and nuclear β-catenin in HepG2 and HUH-7 cells were measured by western blot analysis. Suppression of DKK1 in these cells decreased the expression of WNT1 and β-catenin (a) and the accumulation of nuclear β-catenin (c). Forced expression of DKK1 enhanced the expression of WNT1 and β-catenin (b) and the accumulation of nuclear β-catenin (d) in these cells compared with the corresponding control cells. β-Catenin-shRNA lentiviral vectors were used to deplete β-catenin in DKK1-overexpressing HCC cells, and β-catenin depletion was then confirmed by western blotting (e). Knockdown of β-catenin significantly inhibited the proliferation (f) and tumorigenicity (g, left panel) of DKK1-overexpressing HCC cells. The volumes of tumors in the recipient mice are shown (g, right panel). *P < 0.05