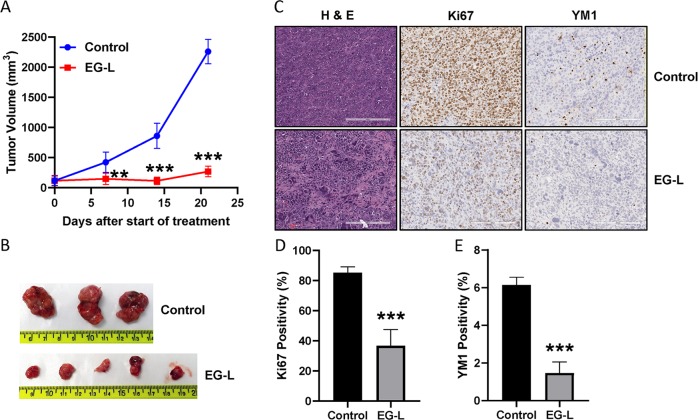
Fig. 5.
Antitumor efficacy of EG-L in an immune-competent mice model of RCC. a 1 × 106 Renca cells were subcutaneously injected into the right flanks of 8 week-old-male Balb/c mice. Tumors were allowed to grow until the average tumor size is ~120 mm3. Then mice were treated with vehicle or EG-L (n = 5 mice per treatment group) 2× per week for 3 weeks. Tumors were measured weekly and tumor volume was plotted to obtain the respective growth curves. EG-L demonstrated significant inhibition compared to the vehicle group. ** and *** denote p < 0.01 and p < 0.001 compared to control, respectively. b Images of the harvested tumors at the end of the experiment. Two tumors from control groups were ruptured before harvest. c Representative images of H&E, Ki67, and YM1 staining of the tumor tissue sections. Bar length = 200 µm. d, e Quantification of Ki67 and YM1 staining respectively. *** denotes p < 0.001 compared to control (n = 3 tumors for control and 4 tumors for EG-L, five spatially different regions from each tumor section).