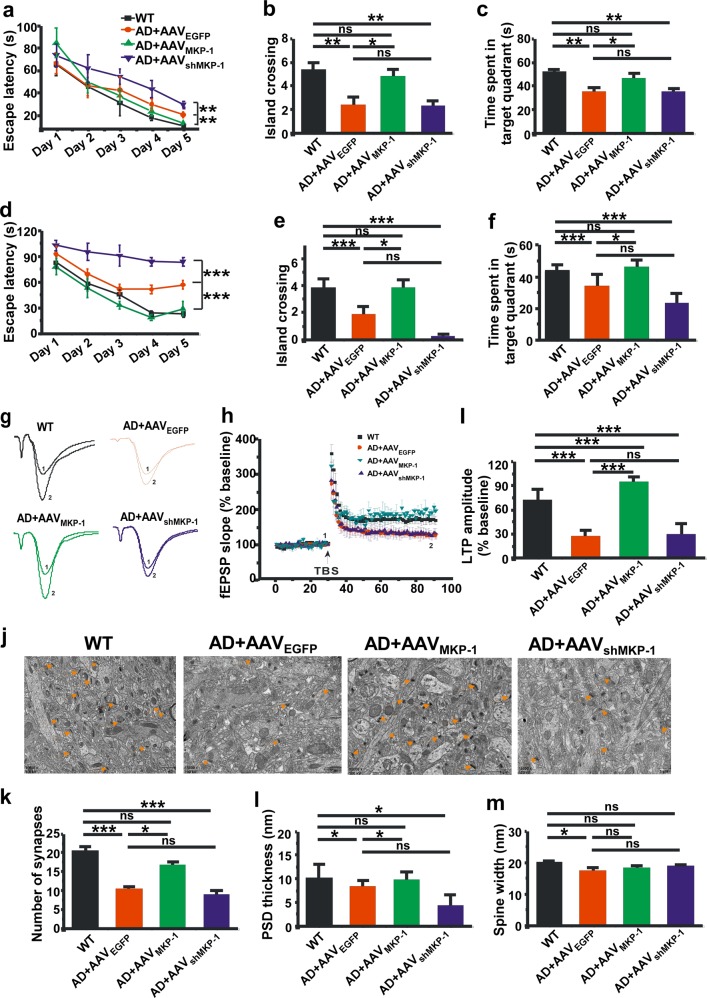
Fig. 6.
MKP-1 alleviated synaptic and memory deficits in APP/PS1 mice. a–c Spatial learning and memory assessed by the Morris water maze test in wild-type (WT) and APP/PS1 transgenic AD mice at the age of 9 months after overexpression of MKP-1 by AAVMKP-1 or knockdown of MKP-1 by AAVshMKP-1. The escape latency to the hidden platform a during the spatial learning period. **p < 0.01 by two-way ANOVA. The number of entries into the platform zone b and the time spent in the hidden platform-located quadrant c during the probe test in absence of the hidden platform in mice. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 by one-way ANOVA. n = 7–12 in each group. d–f Spatial learning and memory as assessed by the Morris water maze test in WT and AD mice at the age of 12 months after overexpression of MKP-1 by AAVMKP-1 or knockdown of MKP-1 by AAVshMKP-1. The escape latency to the hidden platform d during the spatial learning period. ***p < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA. The number of entries into the platform zone e and the time spent in the hidden platform-located quadrant f during the probe test in absence of the hidden platform in mice. *p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA. n = 10 in each group. g–i Hippocampal CA1 LTP recorded from brain slices of WT and AD mode mice at the age of 12 months after overexpression of MKP-1 by AAVMKP-1 or knockdown of MKP-1 by AAVshMKP-1. **p < 0.01 by one-way ANOVA. n = 4 to 10 slices from three mice in each group. j–m Transmission electron microscopic analysis was performed to examine the changes in synapse numbers k, PSD thickness l and spine width m in the hippocampus of WT and AD mice at the age of 12 months after overexpression of MKP-1 by AAVMKP-1 or knockdown of MKP-1 by AAVshMKP-1. *p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA. n = 4 in each group.