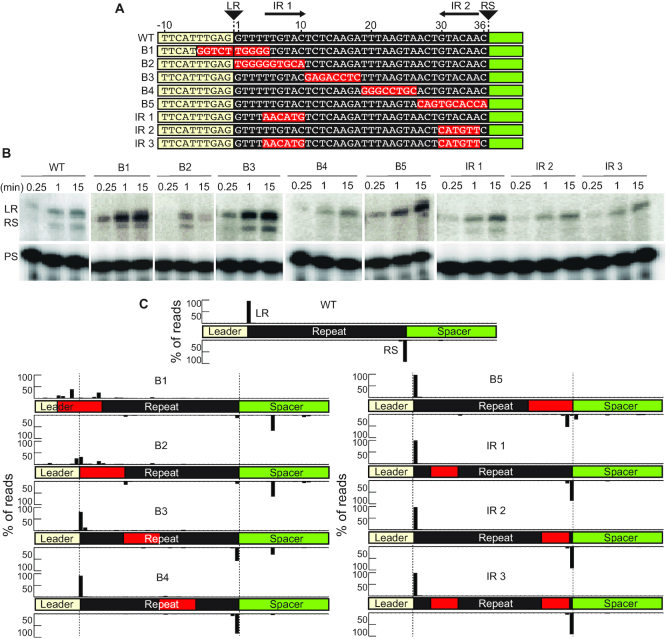
Figure 5.
Repeat sequence mutations affect efficiency and specificity during spacer integration. (A) Annotation of leader and repeat sequence mutations on the linear CRISPR target. Leader-repeat junction (LR), Repeat-spacer junction (RS) and inverted repeats (IR1 and IR2) are indicated. (B) Integration reaction with mutated CRISPR targets taken at time points: 15 s, 1 min and 15 min. (C) High-throughput sequencing analysis of strand-specific integration products; peaks represent the percent of total reads mapped throughout the linear CRISPR target. Top strand and bottom strand libraries were prepared separately and read counts are normalized across strands. Red boxes indicate mutated sequences in the CRISPR target. Nucleotide level resolution of high-throughput sequencing data is provided in Supplemental Figure S4. Range of total number of reads (4,711–12,359).