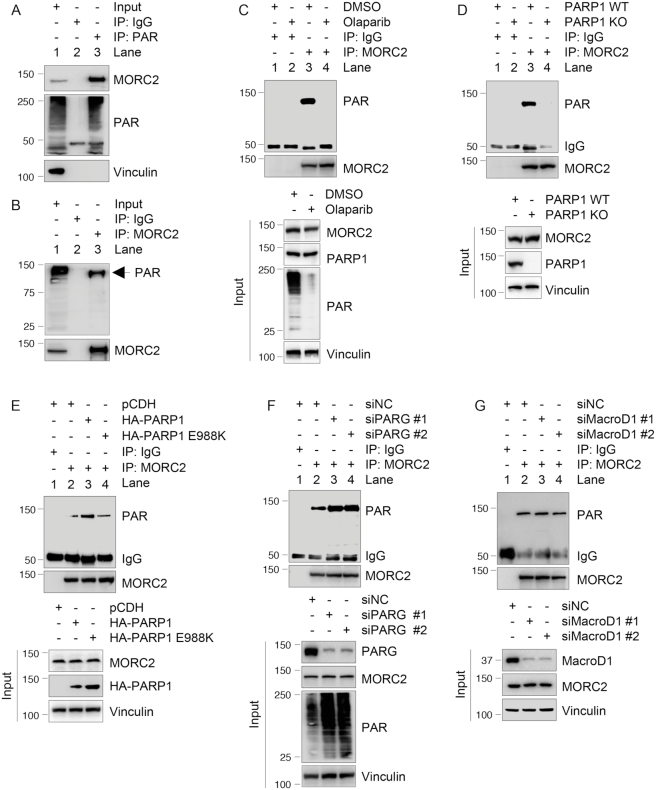
Figure 2.
PARP1 PARylates MORC2. (A and B) Lysates from MCF-7 cells were immunoprecipitated with control IgG or an anti-PAR antibody (A) or an anti-MORC2 antibody (B), followed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (C) MCF-7 cells were treated with or without 5 μM Olaparib for 1 h. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with control IgG or an anti-MORC2 antibody, and the status of PARylation was determined by immunoblotting with an anti-PAR antibody. (D) Lysates from PARP1 WT or KO cells were immunoprecipitated with control IgG or an anti-MORC2 antibody, followed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (E) PARP1 KO cells were transfected with the indicated plasmid DNAs. After 48 h of transfection, lysates were subjected to IP and immunoblotting analysis with the indicated antibodies. (F) MCF-7 cells were transfected with non-targeting control siRNA (siNC) and two different siRNAs targeting PARG. After 48 h of transfection, lysates were subjected to IP and immunoblotting analysis with indicated antibodies. For all in vivo PARylation assays (A–F), PARG inhibitor ADP-HPD (5 μM) was added to the lysis buffer to prevent degradation of PAR. (G) MCF-7 cells were transfected with siNC and two different siRNAs targeting MacroD1. After 48 h of transfection, lysates were subjected to IP and immunoblotting analysis with indicated antibodies.