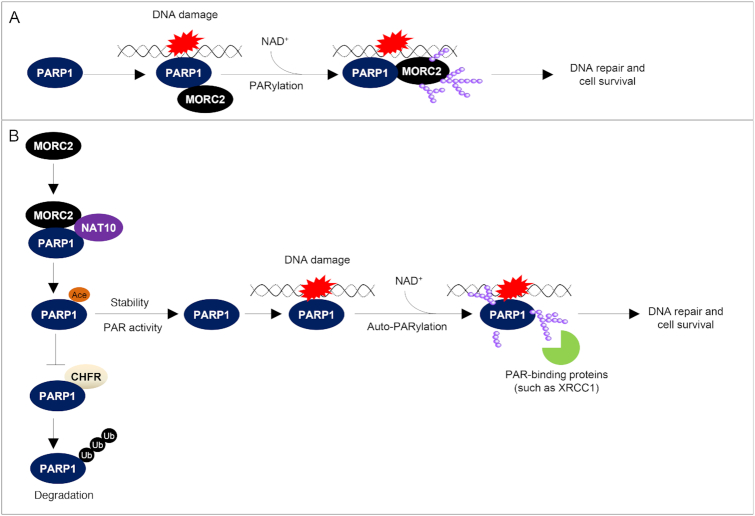
Figure 9.
The proposed working model. (A) Upon DNA damage, PARP1 is recruited to DNA lesions and is rapidly activated to catalyze PARylation of MORC2 using NAD+ as substrate. PARylation of MORC2 enhances its chromatin remodeling activities, thereby promoting efficient DNA repair. (B) MORC2 mediates the interaction between PARP1 and NAT10 and thereby promotes NAT10-mediated PARP1 acetylation at K949, which blocks CHFR-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of PARP1. Consequently, MORC2 regulates DNA damage-induced PAR production at the DNA damage sites and subsequent PAR-dependent recruitment of DNA repair proteins with specific PAR-binding motifs (such as XRCC1) to DNA lesions in response to DNA damage; NAD+, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide.