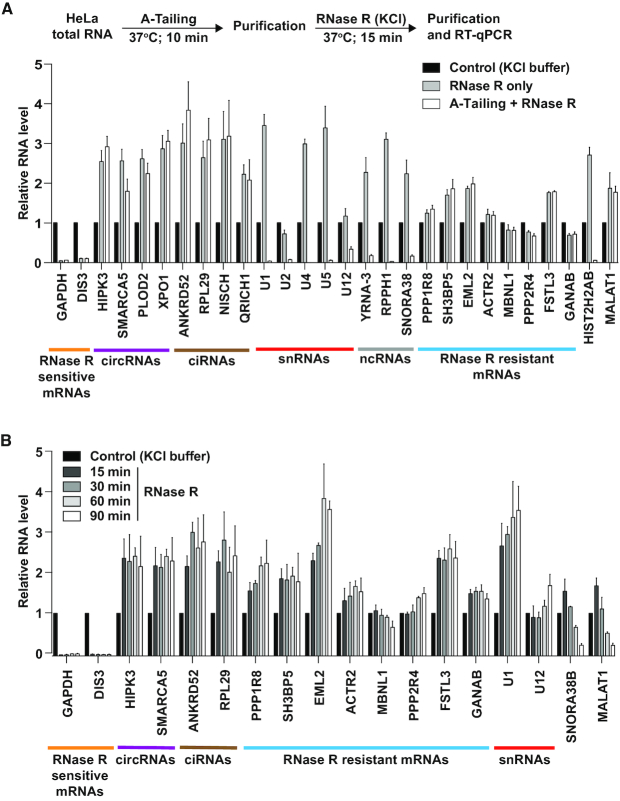
Figure 2.
Many mRNAs remain resistant to RNase R digestion after A-Tailing or longer incubation times. (A) To determine if addition of single-stranded poly(A) tails enables more efficient digestion by RNase R, purified HeLa total RNA was incubated with E-PAP prior to RNase R digestion (white bars). As controls, RNA was incubated only in the reaction buffers (black bars) or subjected to RNase R digestion alone (gray bars). 300 ng of the remaining RNA was used for reverse transcription followed by qPCR to measure the relative abundances of the indicated transcripts. RNase R sensitive mRNAs (orange), circRNAs (purple), ciRNAs (brown), snRNAs (red), ncRNAs (gray), and RNase R resistant mRNAs (blue) are noted. (B) HeLa total RNA was treated at 37°C with buffer (containing KCl) only or RNase R for the indicated amounts of time. 300 ng of the remaining RNA was then used for reverse transcription followed by qPCR to measure the relative abundances of the indicated transcripts. All data were normalized to the control samples and are shown as mean ± SD, n = 3.