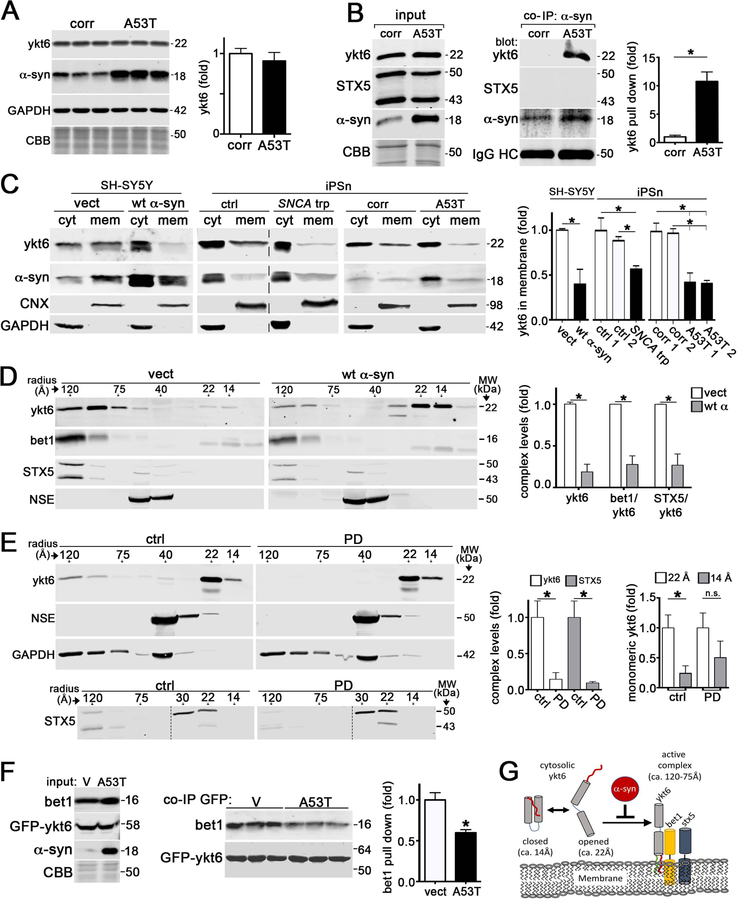
Figure 1. a-Synuclein interacts with ykt6 and disrupts SNARE complex assembly.
A) Western blot of ykt6 in A53T or isogenic corrected (corr) iPSn at day 75 (n=6). GAPDH or Coomassie brilliant blue (CBB) are loading controls. B) Co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) of a-syn and ykt6 in d75 iPSn. Right, quantification (n=3). C) Analysis of cytosolic (cyt) or membrane bound (mem) ykt6 in wt a-syn SH-SY5Y cells, or d90 iPSn from A53T and SNCA triplication (trp) patients compared to multiple controls. Calnexin (CNX) and GAPDH are loading controls (n=3–4). The dashed line indicates cropped out replicates. D) SEC/western blot of ykt6 SNARE complexes in SH-SY5Y cells. Neuron specific enolase (NSE) is a loading control (n=3). E) SEC analysis of PD brain lysates (n=3). F) Co-IP/ western blot from transfected HEK cells (empty vector (v) or A53T a-syn, with GFP-ykt6) (n=3). G) Schematic showing the effects of a-syn on ykt6 function. Farnesyl, red; Palmitoyl, green. Molecular weights (MW) are in kilodaltons (kDa), molecular radius is in angstroms (A). Values are the mean +/− SEM, *p<0.05. See also Figures S1–3.