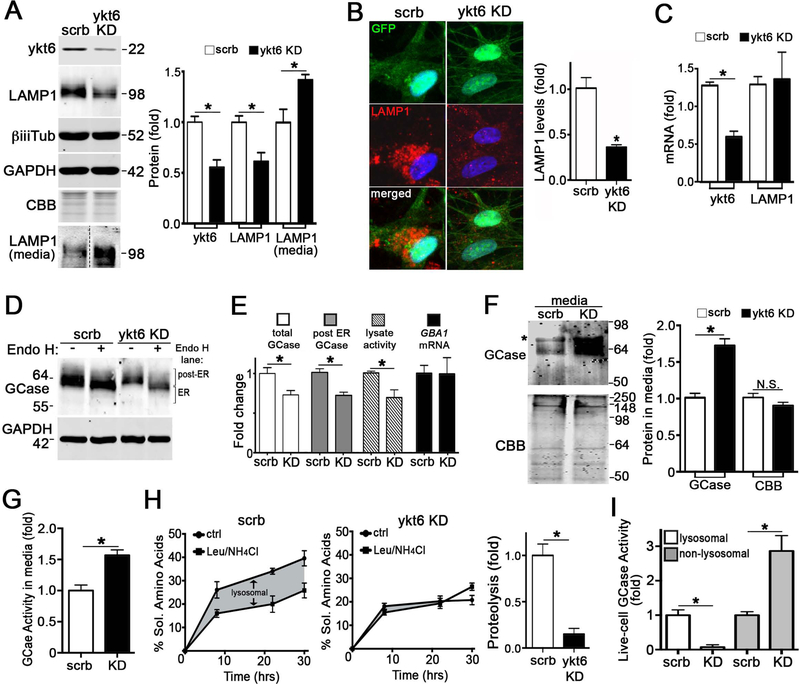
Figure 2. Ykt6 is required for lysosomal function in human midbrain neurons.
A) Lentiviral mediated knock-down (KD) of ykt6 by shRNA (MOI3, dpi7) in control iPSn (scrb, scrambled) followed by western blot of lysates and media. b-iii-tubulin (biiiTub) and GAPDH are loading controls (n=8 lysate, n=3 media). The dashed line indicates cropped out replicates. B) Immunofluorescence of LAMP1 in control iPSn infected with lenti-ykt6 shRNA. GFP indicates infected neurons (n=3). C) mRNA quantification by Q-RT-PCT (n=4). D) Analysis of GCase maturity by endoglycosidase H (endo H) digestion of iPSn lysates. E) Quantification of total and endo H resistant GCase by western blot (from panel D), GCase activity from whole cell lysates, and GBA1 mRNA levels by Q-RT-PCR (n=4). F) Western blot of media from iPSn after ykt6 KD (n=3). *, band detected in media alone. G) GCase activity in media from scrb of ykt6 KD iPSn. H) Proteolysis quantification in living iPSn by measuring soluble (sol.) amino acids released into the media over time. The shaded area shows the response to lysosomal inhibitors, leupeptin (Leu) and NH4Cl (quantified on the right (n=4)). I) GCase activity was measured after ykt6 KD in differentiated SH-SY5Y a-syn cells (n=4). Values are the mean +/− SEM, *p<0.05. See also Figure S4.