Figure 4.
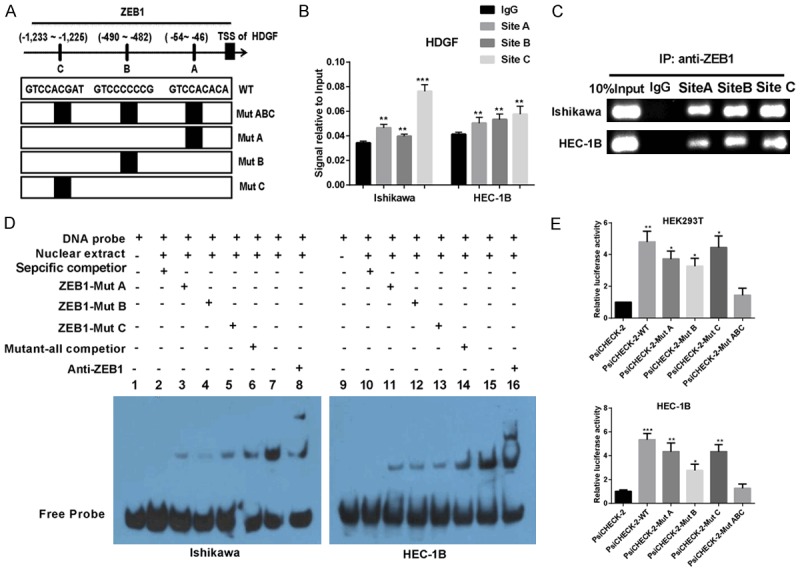
ZEB1 promotes HDGF expression by binding to the promoter region of HDGF. (A) Schematic diagram of the promoter regions of HDGF with the putative ZEB1 TFBSs (A-C), and the structure of the wild-type (WT) and binding sites mutant (MutA, MutB, MutC and MutABC). (B) PCR gel showed amplification of ZEB1-binding sites A and B after ChIP using antibody against ZEB1. (C) The gel figures were accompanied by the locations of molecular weight markers. (D) EMSA result was shown from nuclear proteins extracted from Ishikawa and HEC-1B cells after incubation with individual DIG-ddUTP-labeled oligonucleotide probes (lanes 2-8, 10-16). The free probe of labeled ZEB1 was run in lanes 1 and 9 as a control. A 100-fold excess of unlabelled ZEB1-WT was used to compete with ZEB1 binding (lanes 6 and 14, compared with lanes 2 and 10). A 100-fold excess of unlabelled mutated ZEB1-A, ZEB1-B and ZEB1-C was used to compete with binding of respective labeled probes (lanes 3-5 and lanes 11-13 compared with lanes 2 and 10). (E) Relative luciferase activity of the indicated promoter vectors in HEK293T, and HEC-1B cells transfected with ZEB1 plasmids. Mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
