Figure 7.
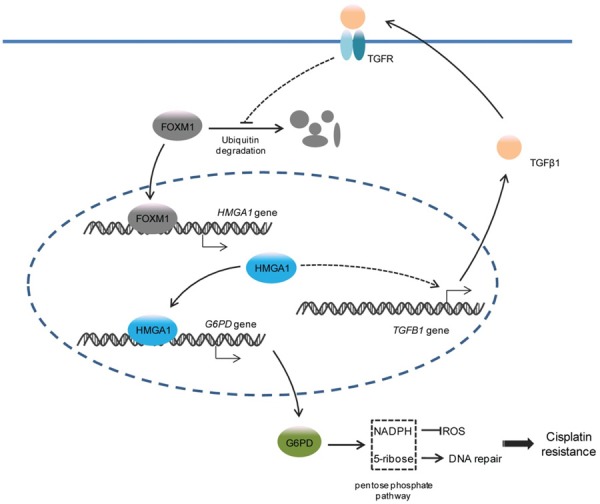
Schema indicating the role of TGFβ1-FOXM1-HMGA1-G6PD axis in cisplatin resistance of NSCLC. TGFβ1 stimulation prevents the ubiquitination and degradation of FOXM1 protein, a transcription factor for HMGA1 gene, thereby activating the transcription of HMGA1. Upregulated HMGA1 further activates the transcription of G6PD to promote the PPP, which supplies NADPH and dNTP against the ROS and DNA damage caused by cisplatin. Moreover, HMGA1 induces the production and secretion of TGFβ1, which in turn enhances TGFβ1 signaling to maintain G6PD expression and chemoresistance.
