Figure 4.
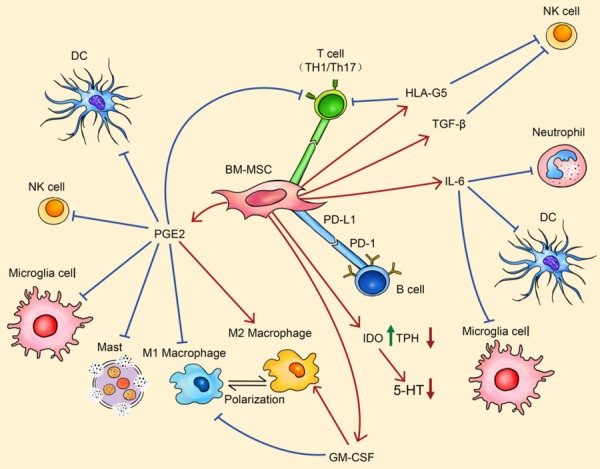
BM-MSC regulates the immune system. By PD-1 mediated cell-cell contact, BM-MSC can inhibit the activation of adaptive immune cells. By secreting PGE2, HLA-G5, TGF-β, IL-6 and GM-CSF, BM-MSC can inhibit the activation of almost every type of immune cells. The regulatory effects can be observed by a pro-inflammatory to anti-inflammatory cell polarization (such as M1 macrophage to M2 macrophage). Meanwhile, IDO secreted from BM-MSC can down-regulate the biosynthesis of 5-HT. Arrows in red indicate stimulative effects while arrows in blue show inhibitory effects. Abbreviations: BM-MSC, bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell; PD-L1, programmed death ligand 1; PD-1, programmed death 1; DC, dendritic cells; NK, natural killer; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; HLA-G5, human leucocyte antigen G5; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; IL-6, interleukin 6; IDO, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; TPH, tryptophan hydroxylase; 5-HT, 5-hydroxytryptamine; GM-CSF, granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor.
