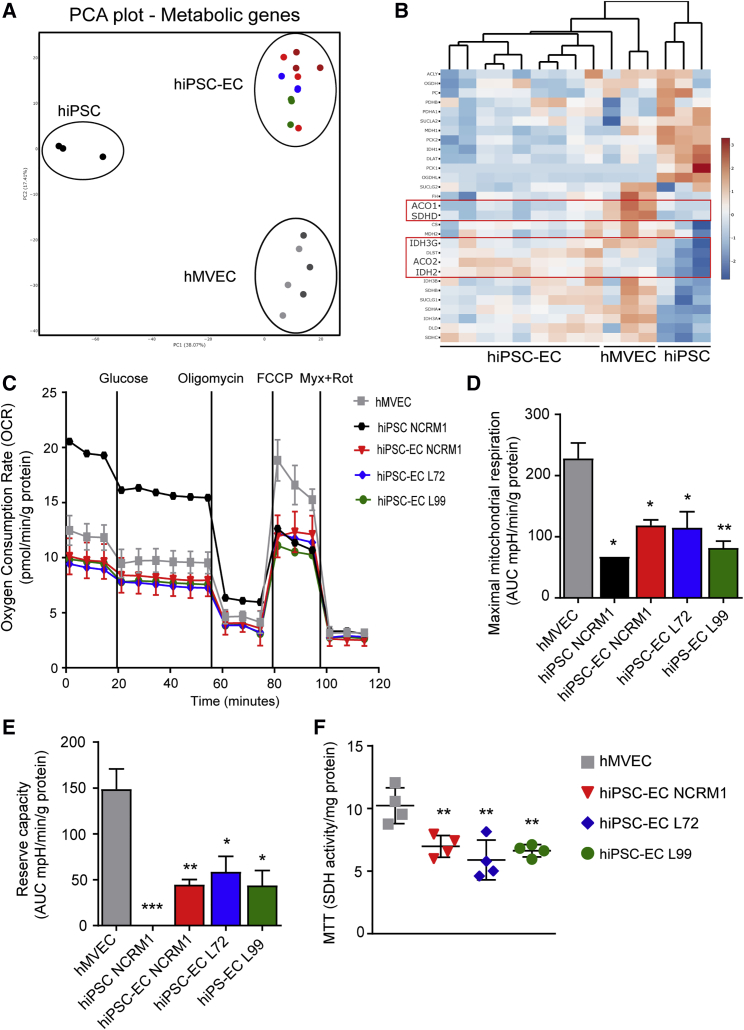
Figure 2.
hiPSC-ECs Have Dysfunctional Mitochondria
(A) PCA plot of expression of all metabolic genes acquired from RNA sequencing of hiPSC NCRM1, hiPSC-ECs NCRM1/L72/L99, and mature ECs (hMVECs).
(B) Heatmap of RNA-sequencing results of metabolic genes involved in the mitochondrial metabolism. Scale bar represents Z scores: blue indicates lower gene expression and red a higher gene expression.
(C–E) Using a Seahorse XF flux analyzer, the oxygen consumption rate (OCR), an indicator of metabolic function, revealed mitochondrial dysfunction in three different hiPSC-EC cell lines (C). Both maximal mitochondrial respiration (D) and mitochondrial reserve capacity (E) were decreased (n = 4).
(F) Mitochondrial activity was also tested by MTT (n = 4).
Values are presented as mean ± SEM of n = 3–5 independent experiments. One-way ANOVA was performed; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗p < 0.0001.