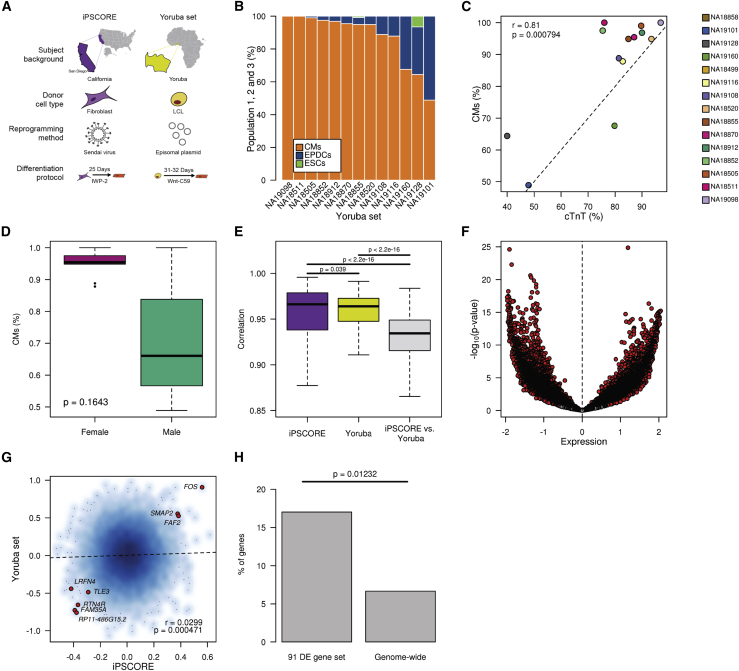
Figure 5.
Validation of Association between iPSC Gene Signatures, Sex, and Differentiation Outcome
(A) Schematic depicting differences between the iPSCORE and Yoruba iPSC samples.
(B) Estimated fractions of CMs and EPDCs for 13 Yoruba iPSC-CM samples from RNA-seq using CIBERSORT (two iPSC-CMs did not have RNA-seq).
(C) Scatterplot showing the correlation between %cTnT and the fraction of cells in population 1 for 13 Yoruba iPSC-CM samples.
(D) Box plots showing the distribution of estimated fraction of cells in population 1 in females and males.
(E) Box plots showing correlation of gene expression in all 184 iPSCORE iPSCs with RNA-seq (purple), 34 Yoruba iPSCs with RNA-seq used for differentiation, and the pairwise comparison of the Yoruba iPSCs against the iPSCORE iPSCs (gray).
(F) Volcano plot showing mean difference in expression levels for all autosomal genes between 14 Yoruba iPSC lines that were successfully differentiated and 125 iPSCORE iPSC-CM-fated lines and p value (y axis, t test). Significant genes are indicated in red.
(G) Smooth color density scatterplot showing gene-expression differences between iPSCs with different fates in 184 iPSCORE iPSCs to the expression differences between iPSCs with different outcomes in Yoruba iPSCs (14 successful versus 20 terminated) (y axis). A positive difference indicates shared overexpression of genes between CM-fated iPSC in iPSCORE and successfully differentiated iPSC in the Yoruba set, whereas a negative difference indicates shared overexpression of genes between EPDC-fated iPSC in iPSCORE and terminated iPSC in the Yoruba set. Of the 91 signature genes that were differentially expressed in the iPSCORE iPSCs based on cell fate, eight had nominally significant expression differences in the same direction in the Yoruba iPSC set (shown in red).
(H) Bar plot showing that the eight iPSCORE differentially expressed genes in (G) with nominal significant expression differences in the same direction (e.g., overexpressed or down regulated) in the Yoruba iPSCs are greater than random expectation.
See also Figure S7.