Figure 3.
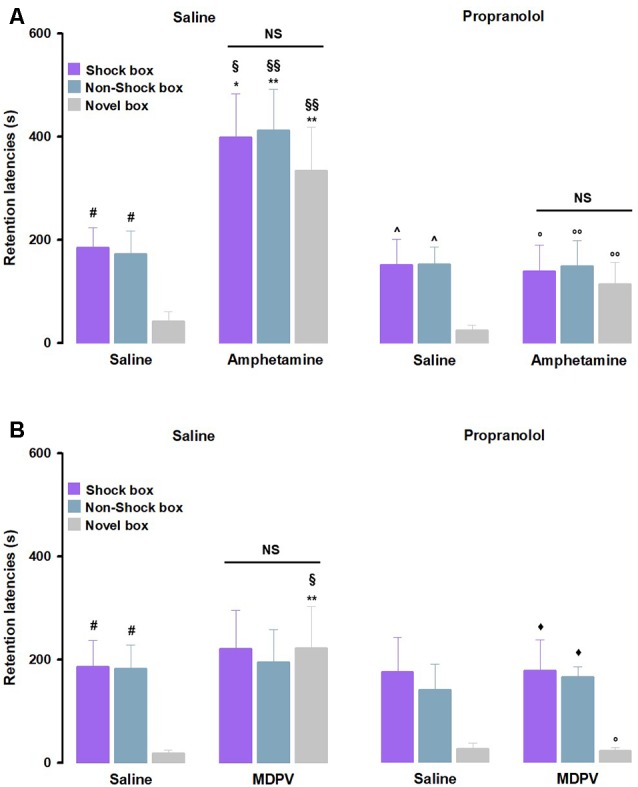
Noradrenergic activation mediates amphetamine and MDPV effects on memory generalization. On the 48-h retention test, rats were sequentially tested in all three contextually modified inhibitory avoidance apparatuses in a random order and their retention latencies were analyzed. (A) Retention latencies of rats treated with propranolol or saline 30 min prior to training together with amphetamine or saline administered immediately after training. Saline alone-treated animals showed longer retention latencies in the Shock box and Non-Shock box compared to those induced in the Novel box, the same happens for the propranolol alone-treated animals. In all three boxes, amphetamine alone-treated rats showed higher retention latencies than saline alone-treated rats and then those exerted by rats given propranolol alone. Retention latencies of the group treated with propranolol together with amphetamine in all three boxes were significantly lower compared to those of amphetamine alone-treated rats. #P < 0.05 saline group latencies in the Shock box or Non-Shock box vs. saline group latencies in the Novel box; ∧P < 0.05 propranolol alone latencies in the Shock box or Non-Shock box vs. propranolol alone latencies in the Novel box; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 amphetamine alone-treated group latencies in the Shock box, Non-Shock box or Novel box vs. saline group latencies in the Shock box, Non-Shock box or Novel box; §P < 0.05, §§P < 0.01 amphetamine alone-treated group latencies in the Shock box, Non-Shock box or Novel box vs. propranolol alone group latencies in the Shock box, Non-Shock box or Novel box; °P < 0.05, °°P < 0.01 propranolol and amphetamine-treated group latencies in the Shock box, Non-Shock box or Novel box vs. amphetamine alone-treated group latencies in the Shock box, Non-Shock box or Novel box; NS, no significant differences (n = 9–13 rats). (B) Retention latencies of rats treated with propranolol or saline 30 min prior to training together with MDPV or saline administered immediately after training. Saline alone-treated animals showed longer retention latencies in the Shock box and Non-Shock box compared to those induced in the Novel box, the same happens for the propranolol together with MDPV-treated animals. In the Novel box retention latencies induced by MDPV alone treatment were significantly longer than those exerted by rats treated with saline alone and propranolol alone. Retention latencies of the group treated with propranolol together with MDPV in the Novel box were significantly lower compared to those of MDPV alone-treated rats. #P < 0.05 saline group latencies in the Shock box or Non-Shock box vs. saline group latencies in the Novel box; ⧫P < 0.05 propranolol together with MDPV latencies in the Shock box or Non-Shock box vs. propranolol together with MDPV latencies in the Novel box; **P < 0.01, MDPV alone-treated group latencies in the Novel box vs. saline group latencies in the Novel box; §P < 0.05, MDPV alone-treated group latencies in the Novel box vs. propranolol alone-treated group latencies in the Novel box; °P < 0.05, propranolol and MDPV-treated group latencies in the Novel box vs. MDPV alone-treated group in the Novel box; NS, no significant differences (n = 8–11 rats).
