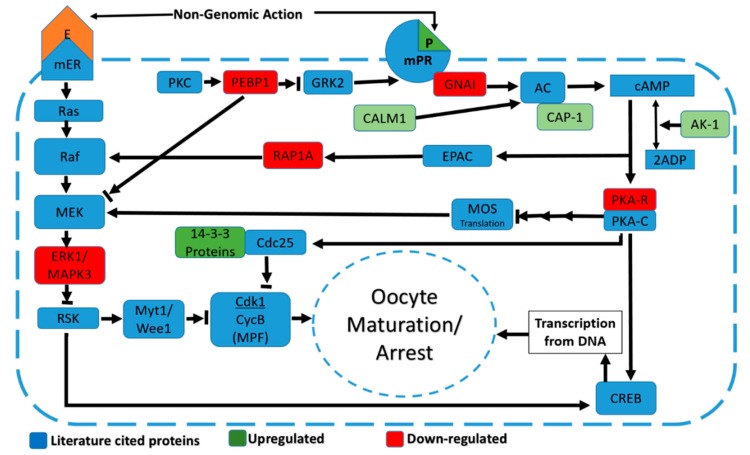
Figure 3.
Differentially abundant proteins related to oocyte maturation/arrest through progesterone and MAPK signaling in ovaries of post-pubertal heifers at the luteal phase compared to pre-pubertal heifers. Green and red tags indicate up- and down-regulated proteins, respectively, and their color intensity is directly related to the fold change level of proteins. Blue tags indicate literature-reported proteins. Progesterone (P); Estrogen (E); Membrane progesterone receptor (mPR); Adenyl cyclase (AC); Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP); G-inhibitory protein (GNAI); Calmodulin-1 (CALM1); Adenlyl cyclase associated protein (CAP-1); Adenylate Kinase-1 (AK-1); Protein kinase-A regulatory subunit (PKAR); Protein kinase-A catalytic subunit (PKAC); Exchange factor directly activated by cAMP (EPAC); Ras related protein-1A (RAP1A); Mos protein (Mos); Cel division cycle protein 25 (Cdc25); Protein Kinase-C (PKC); Phosphatidylethanolanim binding protein (PEBP1); Beta adrenergic receptor kinase2 (GRK2); Membrane Estrogn receptor (mER); Mitogen activated protein kinase (MEK); Mitogen activated protein kinase-3 (MAPK3); Ribosomal S6 Kinase (RSK).; Myelin transcription factor-1 (Myt1); Wee1 like protein kinase (Wee1); Cell division kinase-1 (Cdk1).; Cyclin-B (CycB); cAMP responsive element binding protein (CREB).