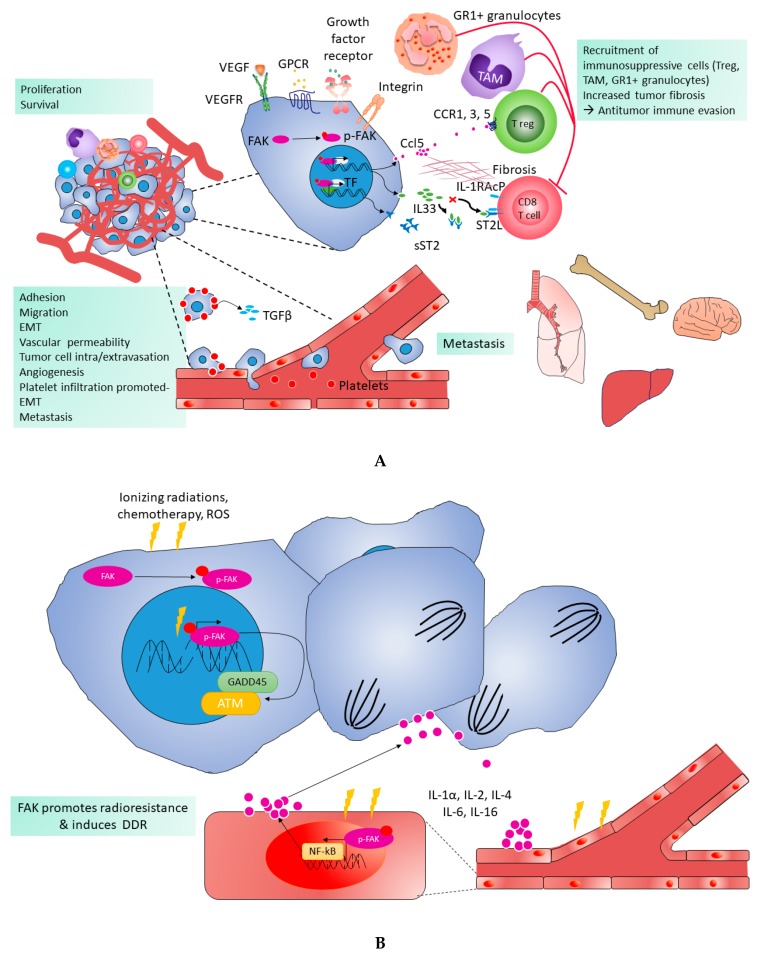
Figure 4.
Pro-tumoral functions of FAK. (A). FAK is triggered off by integrins, G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR), growth factor receptors, and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR). Activated FAK promotes cell proliferation and survival. FAK also contributes to tumor progression and metastasis via cell adhesion, migration, and promotion of epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT). Transient contact between platelets and tumor cells induces TGFβ production by the platelets, which promotes EMT-like transformation and invasive behaviour. In endothelial cell (EC), FAK drives angiogenesis, increases vascular permeability, and regulates platelet extravasation; this facilitates intravasation or extravasation of tumor cells, leading to metastasis. Additionally, FAK induces a tumor protective fibrotic and immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment that promotes antitumor immune evasion. Indeed, FAK induces cytokines (short soluble (sST2), IL33, Ccl5), which lead to the recruitment of immunosuppressive cells, such as regulatory T cells (Treg), tumor-associated macrophages (TAM), and GR1+ granulocytes, as well as to increased tumor fibrosis. Pro-tumoral functions of FAK. (B). Ionizing radiations, chemotherapy, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) increase DNA damage and activate FAK in tumor cells. Activated FAK favors the expression of DNA damage repair (DDR) genes such as Growth Arrest and DNA Damage-inducible 45 (GADD45), Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated (ATM) genes, and Ataxia Telangiectasia and Rad3-related (ATR) genes which play an important role in resistance to drug and radiation. Additionally, in endothelial cells (EC), ionizing radiations activate FAK and NF-kB, which induces the production of various cytokines (IL-1α, IL-2, IL-4 IL-6, IL-16) activating the proliferation of tumor cells. Abbreviations used in the figure and not described in the legend: IL-1RAcP: interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein, ST2L: longer membrane bound form.