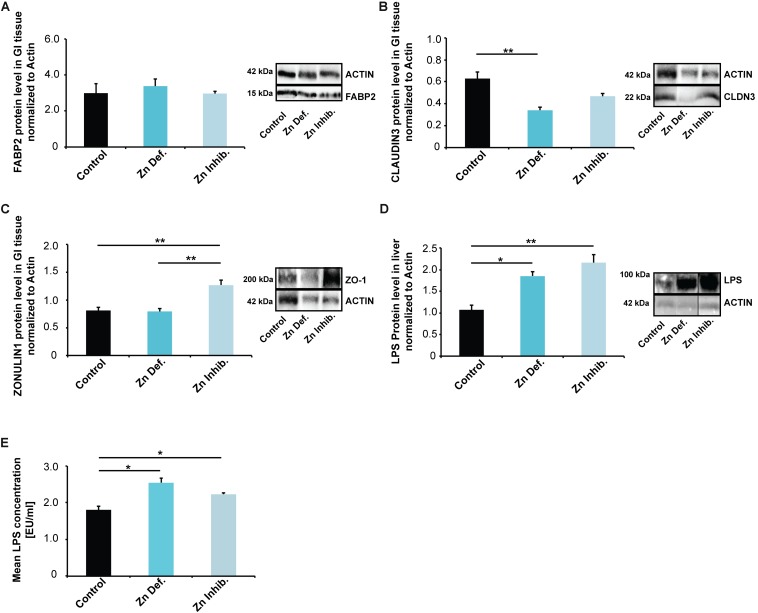
FIGURE 3.
(A–C) Gastro-intestinal epithelium was isolated from three mice per group and protein lysates analyzed using Western blotting. (A) No significant differences in FABP2 were detected. (B) Mice on a Zn deficient diet had significantly reduced levels of CLAUDIN3. (C) ZONULIN1 was significantly increased in mice on Zn inhibitor diet. (D) Liver tissue was isolated from three mice per group and protein lysates analyzed for the levels of E. coli lipopolysaccharide (LPS) using Western blotting. A significant increase in liver LPS is visible in mice on a Zn deficient and Zn inhibitor diet. (E) LPS levels were measured by LAL assay from three mice per group in triplicates. The results show significantly increased LPS levels in liver lysate from mice on Zn deficient and Zn inhibitor diet compared to controls.