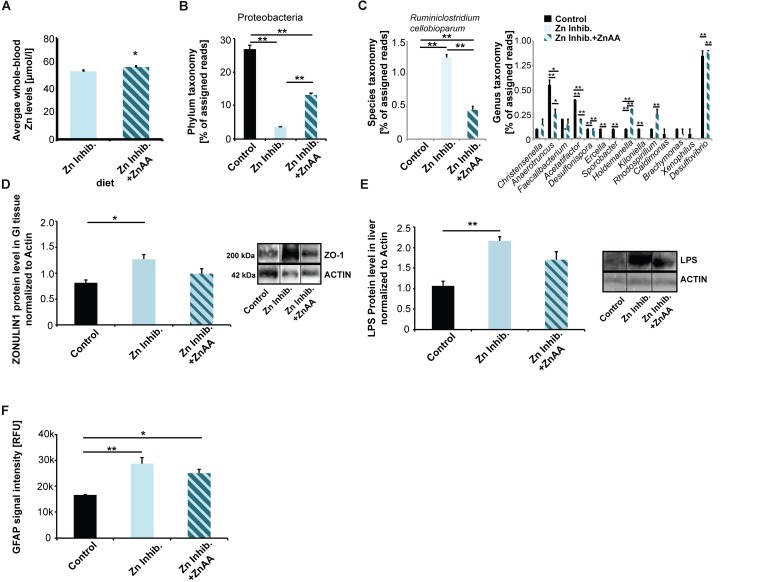
FIGURE 5.
(A) Whole-blood Zn levels of mice measured by AAS in three animals per group. Mice were fed ZnAA supplemented diet (diet 4, Zn Inhibitor + ZnAA). At the end of pregnancy (8 weeks treatment in total), mice on a diet with control zinc levels (35 ppm) but bioavailability of zinc lowered due to the presence of antagonists of absorption (Zn inhibitor) show significantly lower whole-blood zinc levels compared to mice on the same diet with the addition of ZnAAs. (B) Pyrosequencing of 16S rDNA of fecal samples shows that the abundance of Proteobacteria is significantly higher in mice on Zn inhibitor + ZnAA diet compared to mice on Zn inhibitor diet. The levels were still significantly lower compared to mice on the control diet. (C) Left panel: On species level, the almost 10-fold increase in Ruminiclostridium cellobioparum seen in mice on Zn Inhibitor diet was partially prevented. Right panel: Bacteria of the genus Christensiella, Anaerotruncus, Faecalibacterium, Acetatifactor, Desulfonispora, Ercella, Sporobacter, Holdenmanella, Kiloniella, Rhodospirillum, Caldimones, Brachymonas, Xenophilus, and Desulfovibrio were highly reduced or absent in mice on Zn inhibitor diet. Supplementation with ZnAA was able to prevent the reduction/loss for Christensiella, Anaerotruncus, Faecalibacterium, Acetatifactor, Desulfonispora, Holdenmanella, Rhodospirillum, Brachymonas, and Desulfovibrio. (D) GI epithelium was isolated from three mice per group and protein lysates analyzed using Western blotting. Supplementation with ZnAA was able to prevent the significant increase of ZONULIN1 observed in mice on Zn Inhibitor diet. Data for Control and Zn Inhibitor diet has been reused from Figure 3C. (E) Liver LPS is significantly increased in mice on Zn inhibitor diet, but not in mice on Zn inhibitor + ZnAA diet. (F) Brain sections from three animals per group were used for immunohistochemistry. DAPI (labeling cell nuclei) and GFAP or IL-6 were visualized and fluorescent signal intensities from 10 cells in the hippocampus from three sections per animal measured. Mean values show the average of three animals per group. (F) A significant increase in GFAP expression levels can be detected in the brains of mice on the Zn Inhibitor diet compared to control mice. Dietary supplementation with ZnAA slightly, but non-significantly decreased GFAP expression levels.