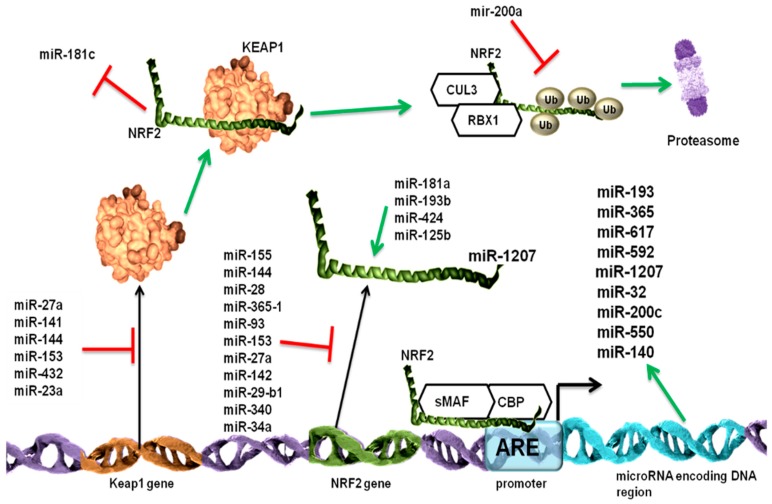
Figure 2.
The Nrf2 pathway is regulated at multiple levels by different microRNAs. The Nrf2 pathway has two important players: the Nrf2 transcription factor and its inhibitor, the Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1) protein. The Nrf2 interaction with Keap1 leads to the further binding of Cullin 3 (Cul3) and RING-box protein 1 (Rbx1) proteins and the ubiquitination of Nrf2 proteins, resulting in proteasomal degradation. If Nrf2 does not bind to Keap1, it binds to the antioxidant response element (ARE)-containing promoter regions, and, by forming a complex with small V-Maf Avian Musculoaponeurotic Fibrosarcoma Oncogene (sMaf) and cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB)-binding protein (CBP), it leads to the further activated transcription of its targeted genes. MicroRNAs suppress Keap1/Nrf2 signaling at multiple levels. MiR-27a, miR-141 miR-144, miR-153, miR-200a, miR-432, and miR-23a repress the translation of Keap1 messenger RNA (mRNA), thus allowing for Nrf2 activation. MiR-155, miR-144, miR-28, miR-365-1, miR-93, miR-153, miR-27a, miR-142, miR-29-b1, miR-340, and miR-34a, either through direct repression of Nrf2 mRNA in a Keap1-independent manner or by enhancing the Keap1 cellular level, inhibit Nrf2 activity. MiR-181a, miR-193b, miR-424, and miR-125b stimulate Nrf2 activation most probably by repressing its activators. The Keap–Nrf2 interaction leads to the repression of miR-181c, which is involved in the Nuclear factor kappa light chain enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) signaling pathway. MiR-200a inhibits the ubiquitination of Nrf2, thus protecting it from degradation. Nrf2, in addition to the classical targeted genes, can also stimulate the expression of the miRNA-encoding DNA region. The Keap1 protein structure was taken from the http://www.rcsb.org database [156,157] and the Nrf2 structure was taken from the http://www.cisreg.ca/tfe/structures/NFE2L2-4780-1jnmB.pdb.png online tool.