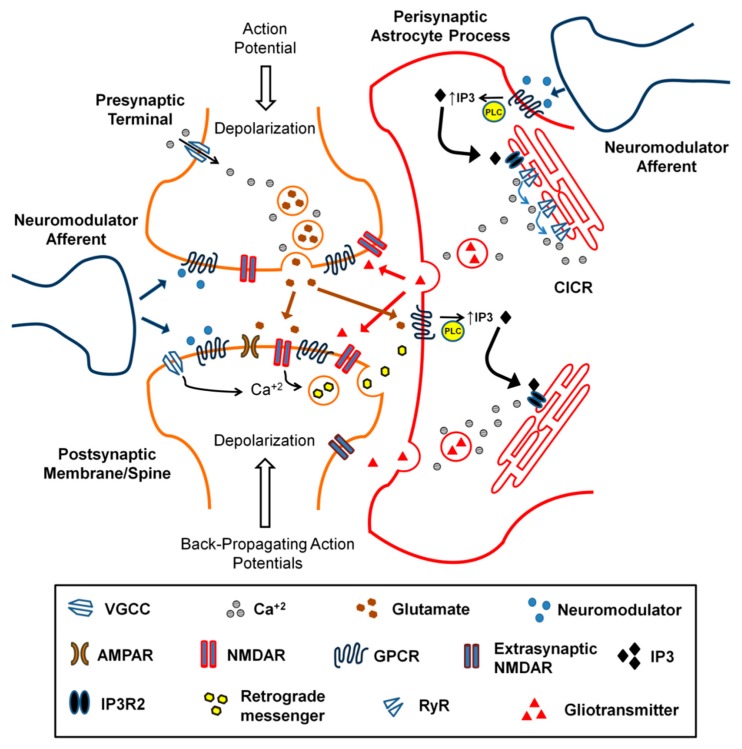
Figure 2.
A schematic representation of astrocytic synaptic coverage and neuromodulatory inputs. Astrocytes are able to detect and respond to both synaptic activity and neuromodulatory afferent signals. Neuromodulators and neuron-released transmitters (presynaptic and postsynaptic retrograde messengers) activate associated receptors on perisynaptic astrocyte processes leading to intracellular calcium signalling and subsequent induction of gliotransmitter release to modulate local activity and synaptic plasticity. Similarly, neuromodulatory signals can target neurons, astrocytes or both; hence, neuromodulators transmit behaviour-related signals to induce neuronal activity directly and/or through astrocytes.