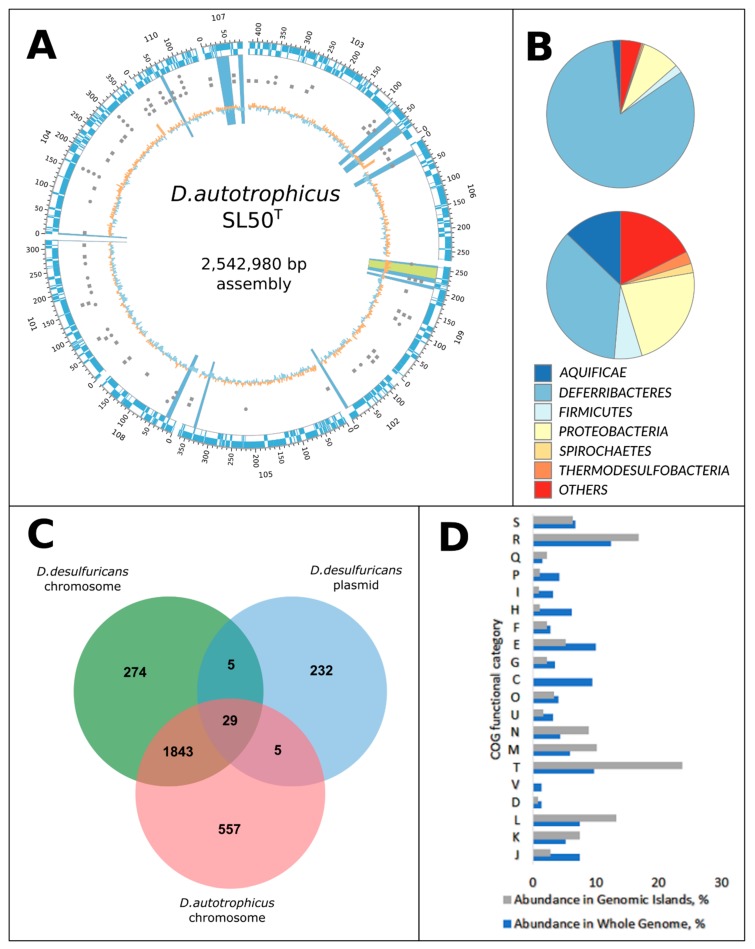
Figure 1.
Genomic features of Deferribacter autotrophicus SL50T. (A) Circular map of the genomic features of D. autotrophicus. Rings from outside to inside: contig ID (corresponding to the locus number suffix, e.g., Ga0300908_101); genomic coordinates in the corresponding contig; plus-strand CDS (light blue); minus-strand CDS (light blue); GI-related features—tRNAs (grey circles) and transposases (grey squares); GC-content, relative to the average GC-value. Genomic islands are shown as light-blue sectors; prophage is shown as the light green sector. Contigs of D. autotrophicus were ordered according to the alignment of the publicly available D. desulfuricans genome (NC_013939) with the contig ordering tool from the MAUVE genome alignment package [19]; (B) Genome-wide (top) and genomic islands (bottom) taxonomic distribution of proteins best blast hits; (C) Venn diagram of protein orthologs shared by the assembly of D. autotrophicus chromosome and plasmid of D. desulfuricans. Orthology analysis of was performed with OrthoVenn2 web server [14] using 0.01 blast e-value and 1.5 orthoMCL grain value. Numbers indicate shared or unique protein clusters and singleton proteins. (D) Distribution of COG functional categories in the genome (blue bars) and in genomic islands (grey bars). Functional categories are represented as follows: Amino acid transport and metabolism [E], Carbohydrate transport and metabolism [G], Cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning [D], Cell Motility [N], Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis [M], Coenzyme transport and metabolism [H], Defense mechanisms [V], Energy production and conversion [C], Function unknown [S], General function prediction only [R], Inorganic ion transport and metabolism [P], Intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport [U], Lipid transport and metabolism [I], Mobilome: prophages, transposons [X], Nucleotide transport and metabolism [F], Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones [O], Replication, recombination, and repair [L], Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport, and catabolism [Q], Signal transduction mechanisms [T], Transcription [K], Translation, ribosomal structure, and biogenesis [J].