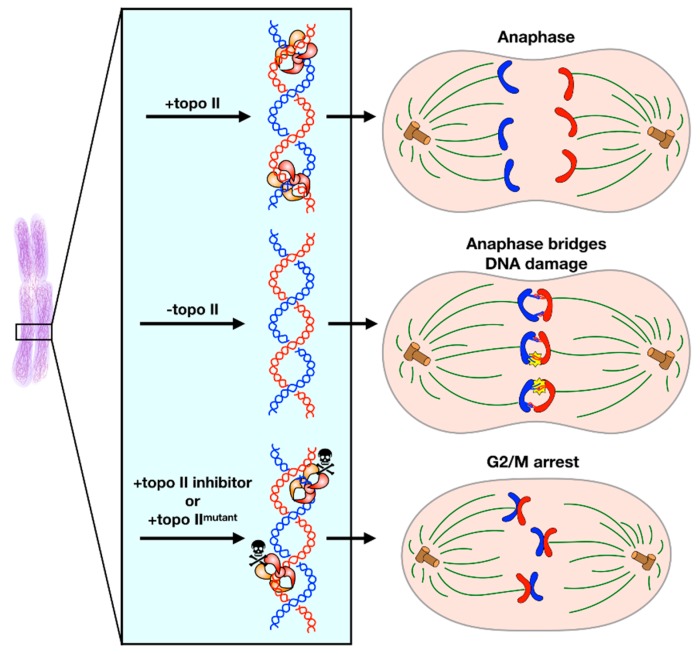
Figure 3.
Decatenation Checkpoint. (Upper) Under normal conditions, topo II completes decatenation of intertwined sister chromosomes immediately before anaphase to allow for faithful chromosome segregation. (Middle) If topo II is absent, the cell cannot sense that sister chromosomes are catenated and will proceed into anaphase. Anaphase entry in this condition leads to the formation of anaphase bridges and DNA damage. (Lower) If topo II activity is inhibited by a small molecule or a mutation that impedes enzymatic activity, the cell will arrest in G2/M phase until either decatenation is complete or the cell enters apoptosis.