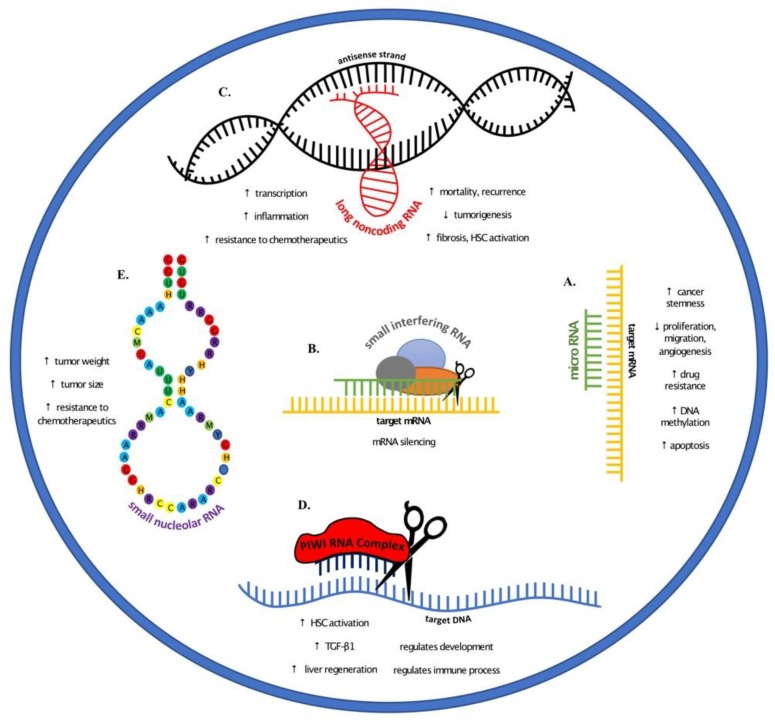
Figure 1.
Noncoding RNAs and their roles in liver cancer elucidated through various animal models. (A) microRNAs regulate cancer progression through increasing stemness, drug resistance, and DNA methylation. Conversely, microRNAs play a role in decreased proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis, and increased apoptosis. (B) Small interfering RNAs target messenger RNA and silence their transcription. (C) The role of long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) varies with increased transcription, inflammation, resistance to chemotherapeutics, and fibrosis. In addition to increased HSC activation, there are higher incidence of mortality and cancer recurrence. Other lncRNAs have also been indicated in decreased tumorigenesis. (D) PIWI RNA have been shown to activate HSCs and increase TGF-β1 expression and liver regeneration, in addition to regulating immune processes and development. (E) Small nucleolar RNAs provide resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs and have been shown to increase tumor size and weight.