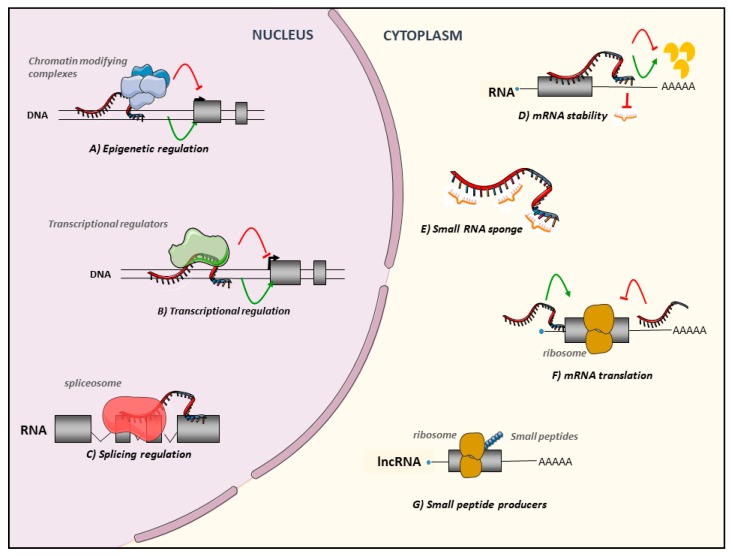
Figure 1.
Long Noncoding RNAs: a truly large and multifaced family. Nuclear lncRNAs are implicated in (A) Epigenetic regulations, leading to the recruitment of activator/repressor chromatin modifying complexes on their target promoters, (B) Transcriptional regulations, guiding or preventing the recruitment of transcription factors on the promoters of their targets or on other active chromatin sites, (C) Splicing regulations regulating recruitment of spliceosome partners. Cytoplasmic lncRNAs also affect post-transcriptional steps regulating (D) mRNA stability modulating degradation, positively or negatively or acting as (E) small regulatory RNA sponges. Finally, they regulate (F) mRNA translation. LncRNAs can also be (G) small peptide producers.