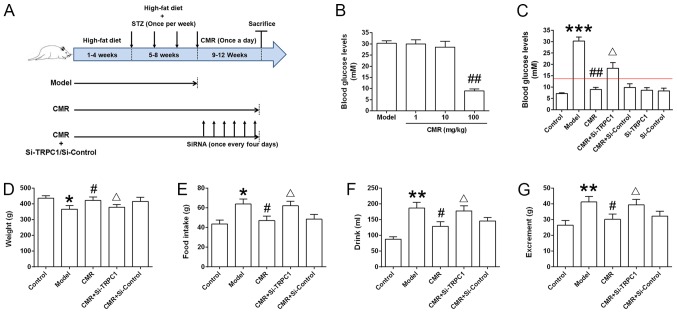
Figure 1.
Effect of CMR treatment on the blood glucose levels of diabetic rats. (A) Schematic diagram of the experimental procedure. Rats were fed a high-fat diet for 8 weeks. During weeks 5–8, STZ (30 mg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally once a week. The rats were then subjected to 4 continuous weeks of CMR (once a day) with or without the tail vein delivery of si-TRPC1 of si-control (once every 4 days). The rats were sacrificed and the samples were collected 24 h after the last CMR treatment. (B) The blood glucose levels between the diabetic model and CMR treatment groups, including low (1 mg/kg), moderate (10 mg/kg) and high (100 mg/kg) doses of CMR, were measured through the tail vein using a blood glucose meter. (C) At the end of the experiment, the blood glucose levels of rats from the different groups were measured and statistically analyzed. The red line indicates a blood glucose level of 13.9 mM. (D) Weight, (E) food intake, (F) drinking water and (G) excrement were monitored. The parameters refer to the average value per rat in the different groups (n=5 per group). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs. control; #P<0.05 and ##P<0.01 vs. model; ΔP<0.05 vs. CMR. STZ, streptozotocin; CMR, Cortex Mori Radicis extract; TRPC1, transient receptor potential canonical channel 1; si-, small interfering RNA.