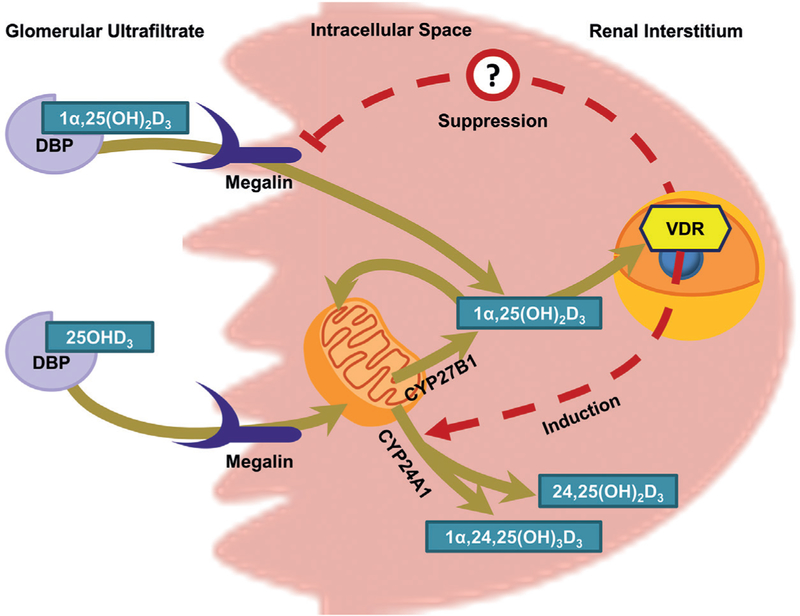
Fig. 9: Role of megalin in the maintenance of renal vitamin D metabolite homeostasis.
In PTECs, apically-localized megalin reclaims DBP-bound vitamin D metabolites from the glomerular ultra-filtrate. Resorbed 25OHD3 is then shuttled to the mitochondria for either CYP24A1-mediated inactivation or CYP27B1-mediated bioactivation. Intracellular 1α,25(OH)2D3, whether generated within the PTECs mitochondria or resorbed directly from the tubular lumen, can then undergo metabolic inactivation, enter systemic circulation to mediate endocrine effects or exert VDR-dependent intracrine effects within the PTECs. Intracrine effects include the compensatory upregulation of CYP24A1 gene expression. Megalin gene expression may also be a target for 1α,25(OH)2D3,- mediated suppression in humans.