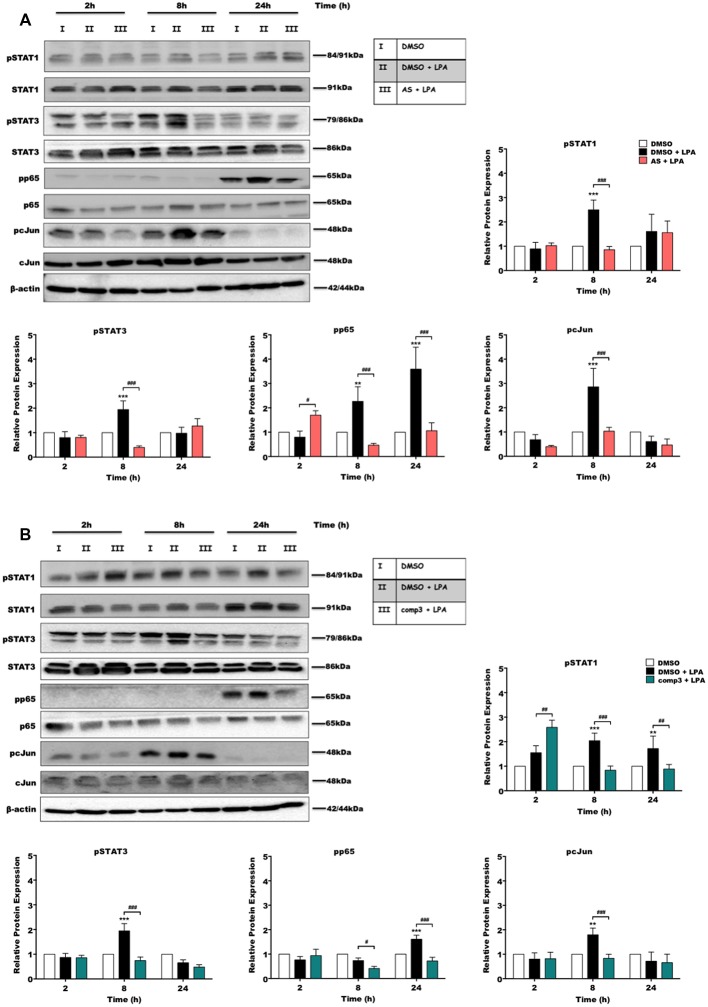
Figure 2.
AS2717638 and compound 3 attenuate lysophosphatidic acid (LPA)-induced phosphorylation of pro-inflammatory transcription factors. BV-2 microglia cells were cultured in 6-well plates and serum-starved o/n. Cells were treated with DMSO, DMSO plus LPA (1 μM), and LPA (1 μM) in the presence of (A) AS2717638 (0.1 μM) or (B) compound 3 (1 μM) for the indicated time periods and cell protein lysates were collected. The phosphorylation states along with the total levels of STAT1, STAT3, p65-NF-kB, and c-Jun were detected using Western blotting. If two bands appeared for one protein [e.g., (p)STAT3] both bands were included in the densitometric evaluation. Protein/loading control ratios were normalized to the ratio of unstimulated microglia (mean value of DMSO controls was set to 1). One representative blot out of three separate experiments and the densitometric analysis of each protein expression from three independent experiments is presented (**p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 compared to DMSO-treated cells; #p < 0.05; ##p < 0.01; ###p < 0.001 each inhibitor compared to LPA-treated cells; one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction).