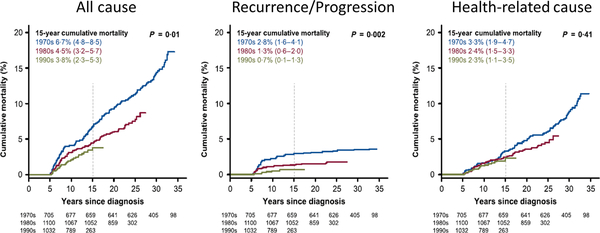
Fig 1.
All-cause and cause-specific cumulative mortality among 5-year survivors of childhood cancer, according to decade. Shown is the cumulative incidence of death from any cause (A), from disease recurrence or progression (B), and from any health-related cause (C) among 34 033 patients who survived at least 5 years after childhood cancer for which treatment was initiated during the period from 1970 to 1999. The values in parentheses are 95% confidence intervals. The vertical dashed lines indicate 15-year mortality. P values are for the comparisons among the three decades. From New England Journal of Medicine, Armstrong, G.T., Chen, Y., Yasui, Y., Leisenring, W., Gibson, T.M., Mertens, A.C., Stovall, M., Oeffinger, K.C., Bhatia, S., Krull, K.R., Nathan, P.C., Neglia, J.P., Green, D.M., Hudson, M.M. & Robison, L.L., Reduction in Late Mortality among 5-Year Survivors of Childhood Cancer. 374, 833–842. Copyright ©2016 Massachusetts Medical Society. Modified with permission from Massachusetts Medical Society.