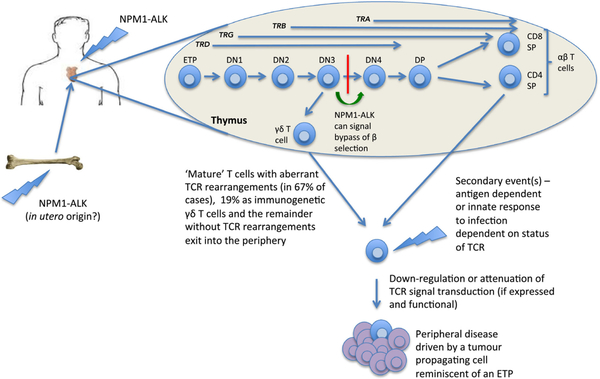
Fig 15.
A thymic origin for ALCL. In this model, the t(2;5) or variant translocation occurs in haemopoietic stem cells or thymic progenitors whereby NPM1-ALK is permissive of cellular survival in the thymus despite aberrant TCR rearrangements. These ‘primed’ cells may go undetected until a secondary event(s) occurs that leads to clonal expansion and tumour development. This event may be induced as a consequence of an inflammatory response as evidenced by ALCL in the context of insect bites but might also be initiated in an innate manner. ALCL, anaplastic large cell lymphoma; DN, double negative thymocyte; DP, double positive thymocyte; ETP, early thymic progenitor; SP, single positive; TCR, T-cell receptor. From Turner, S.D., Lamant, L., Kenner, L. & Brugieres, L. (2016) Anaplastic large cell lymphoma in paediatric and young adult patients. Br J Haematol, 173, 560–572. © 2016 John Wiley and Sons Inc.