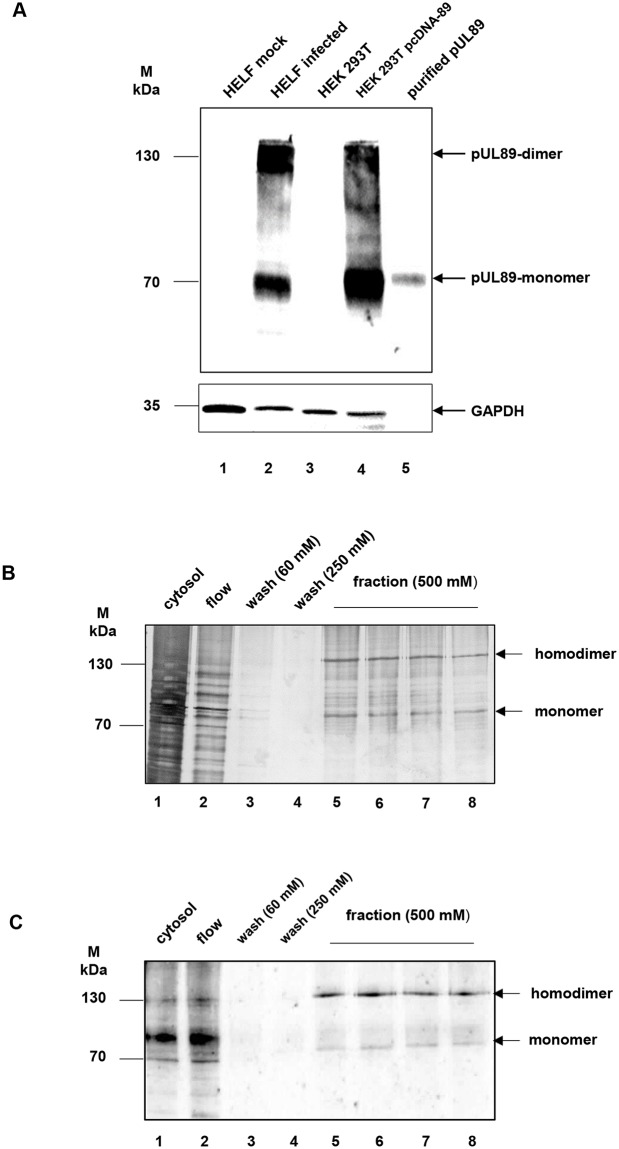
Fig 2. Purification of pUL89 from transfected HEK 293T cells.
(A) Characterization of the monoclonal antibody against pUL89 (mAbUL89). Mock-infected (lane 1) and infected HELF (lane 2), HEK 293T (lane 3), HEK 293T transfected with pcDNA-89 (lane 4) and purified pUL89 (lane 5) were separated by 10% SDS–PAGE and transferred to nitrocellulose. The immunoblot was reacted with mAbUL89. GAPDH served as a loading control. (B) Silver staining of purification of pUL89. Lane 1, cytosol; lane 2, flow; lane 3–4, wash fractions (60 mM and 250 mM imidazole), lane 5–8 fraction with eluted pUL89 (500 mM imidazole). (C) Immunoblot of purification of pUL89. Lane 1, cytosol; lane 2, flow; lane 3–4, wash fractions (60 mM and 250 mM imidazole), lane 5–8 fraction with eluted pUL89 (500 mM imidazole). Probes were subjected to SDS-Page followed by silver staining or immunoblot analysis with anti-pUL89 (mAbUL89). Markers (kDa) are indicated on the left, the position of pUL89 on the right.