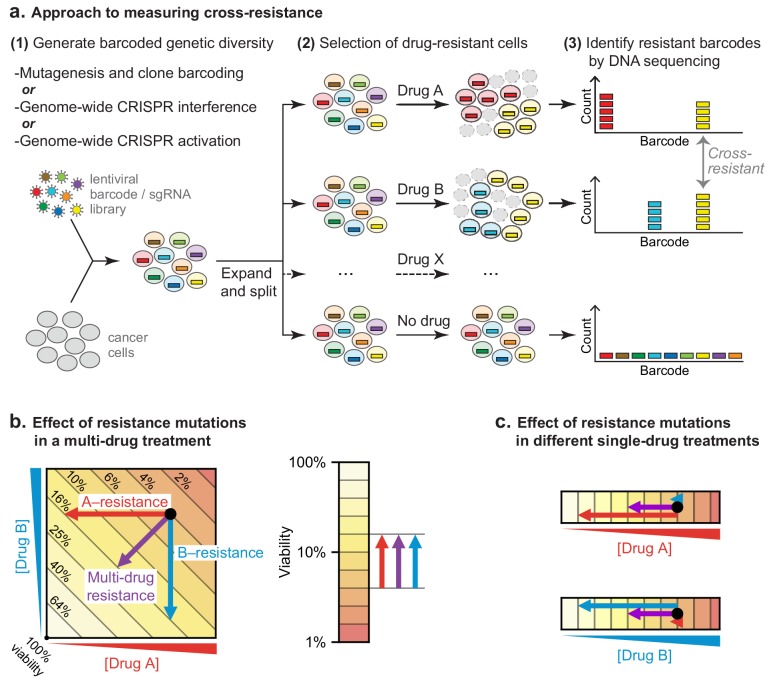
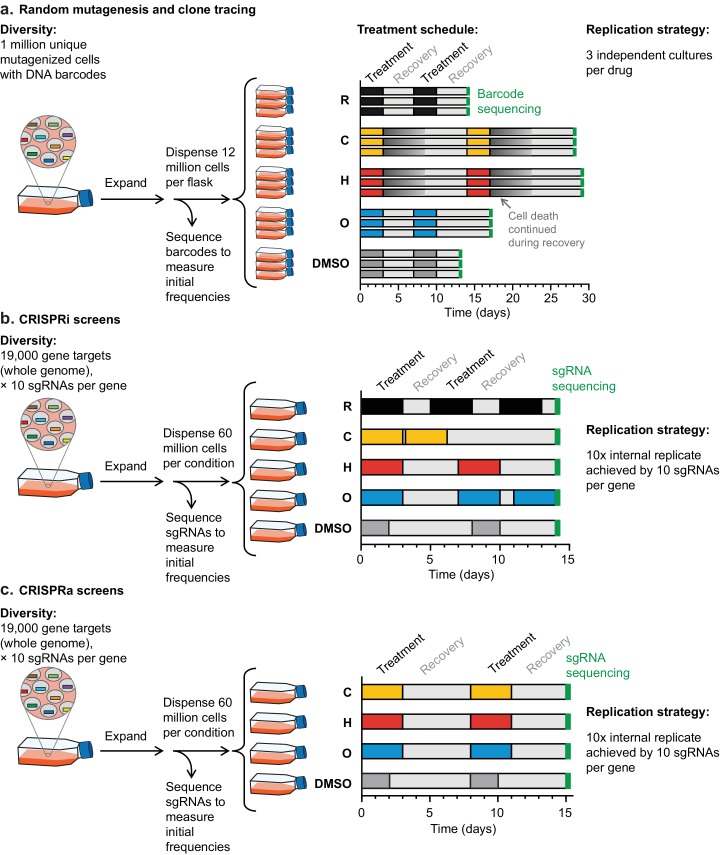
Figure 3. Strategy for measuring cross-resistance between drugs.
(a) Cells were mutagenized and barcoded using one of three approaches: (i) random mutagenesis and clone tracing, (ii) knockdown by CRISPRi or (iii) overexpression by CRISPRa. 106 mutagenized clones or genome-wide CRISPRi/a libraries were expanded and split into replicate cultures, treated with single drugs, and DNA barcodes/sgRNAs abundance was measured by DNA sequencing. The resistance of cells to drug treatment was scored based on the degree of barcode enrichment, and cross-resistance was determined by significant enrichment in two or more drug treatments. (b) Schematic showing importance of selecting for resistance to single drugs not cocktails. Arrows: resistance is analogous to lower drug concentration and moves cells to different coordinates; cross-resistance (purple arrow) has same net effect as more penetrant single-drug resistance mutations (red, blue arrows). (c) By selecting mutations on single drugs the magnitude of the effect on each drug is known.