Fig. 2.
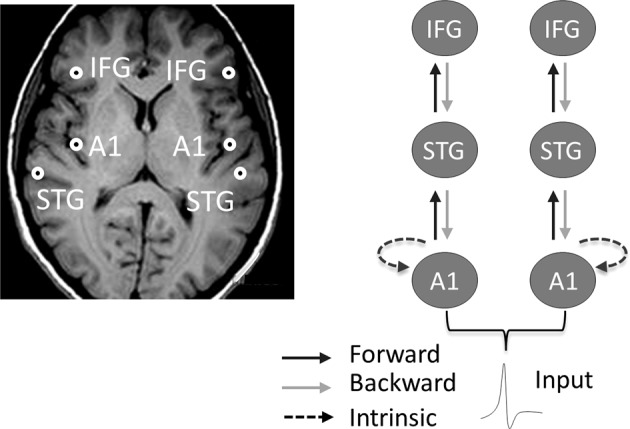
Left. The MMNm arises from bilateral sources over primary, secondary auditory cortex (superior temporal gyrus, STG), and inferior frontal gyri (IFG) [150]. Right. Dynamic causal modeling shows that the MMN results from changes within and among these cortical sources [151]. Forward connections can be conceptualized as bottom-up processes transmitting sensory information from A1 to higher cortical levels and convey prediction errors (MMN). Backward connections represent top–down predictions based on prior sensory experience and explain away prediction errors (deviance detection). In the safe context, the MMN is mediated by changes in both extrinsic feedforward and feedback connectivity, as well as intrinsic connectivity (not shown). Anxiety induced by threat of shock suppresses feedback connectivity. The anxiolytic alprazolam reestablishes feedback connectivity (not shown)
