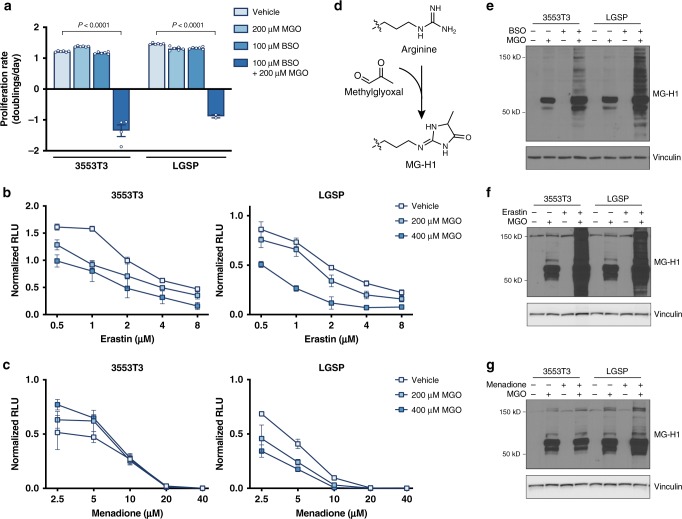
Fig. 3. Glutathione depletion sensitizes NSCLC cell lines to methylglyoxal.
a Proliferation rate of 3553T3 and LGSP cells cultured in standard media or in media containing the indicated amount of methylglyoxal (MGO) or buthionine sulfoximine (BSO), an inhibitor of glutathione synthesis. Cells treated with BSO had been pre-treated with BSO for 48 h prior to the initiation of the experiment. The P values were calculated by unpaired, two-tailed t-test (n = 6). b, c Effect of the indicated concentration of erastin, which depletes intracellular glutathione by inhibition of system xc− (b), and menadione, which induces formation of reactive oxygen species (c), on cell viability as assessed using the CellTiter-Glo Luminescence Assay in 3553T3 and LGSP cells cultured in standard media or in media containing the indicated doses of methylglyoxal (n = 3). d Schematic detailing how methylglyoxal can react non-enzymatically with arginine to form the hydroimidazolone MG-H1. e Western blot analysis of lysates from 3553T3 and LGSP cells that had been incubated with 200 μM of methylglyoxal, 100 μM of BSO, or both for 24 h using an antibody raised against the MG-H1 epitope. Cells treated with BSO had been pre-treated with BSO for 48 h prior to the initiation of the experiment. f, g Western blot analysis of lysates from 3553T3 and LGSP cells to assess accumulation of proteins containing MG-H1 epitopes following 24 h of culture in standard media or in media containing 200 μM methylglyoxal, 10 or 5 μM erastin (3553T3, LGSP respectively), or both as indicated (f), or 200 μM methylglyoxal, 2 or 1 μM menadione (3553T3, LGSP respectively), or both as indicated (g). Values in panels a–c denote mean ± SD.