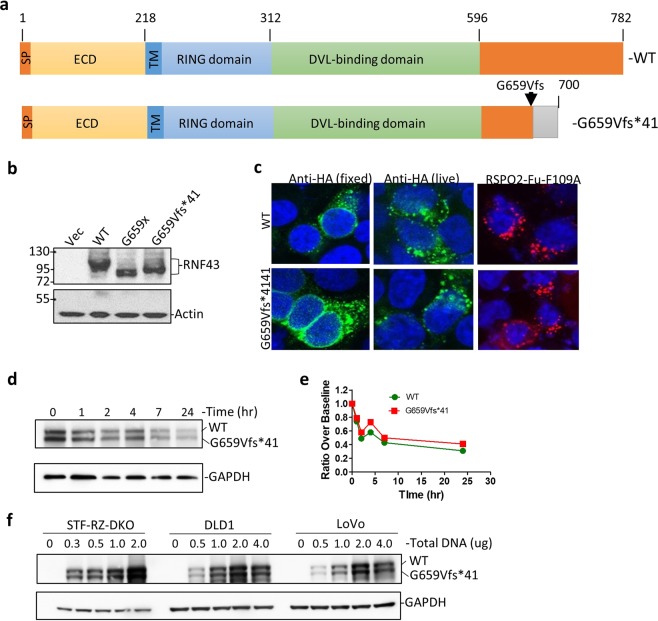
Figure 2.
Expression, localization, RSPO binding, and stability of RNF43-G659Vfs*41 is similar to RNF43-WT. (a) Schematic diagram of domain structures of RNF43-WT and RNF43-G659Vfs*41. ECD, extracellular domain; TM, transmembrane domain; RING, RING E3 ligase domain. (b) WB of HEK293T cells transfected with vector control (Vec), or HA-tagged RNF43-WT, -G659x, or -G659Vfs*41 using anti-HA antibody. (c) Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy of STF-RZ-DKO cells transfected with RNF43-WT and -G659Vfs*41 and stained with mouse anti-HA and Alexa488-labeled anti-mouse IgG (green), or incubated with RSPO2-Fu-F109A-Fc followed by staining with Alexa-555-labeled anti-human IgG (red). Nuclei were counter-stained with TO-PRO-3 Iodide (blue). (d) Anti-HA WB of STK-RZ-DKO cells co-transfected with RNF43-WT and –G659Vfs*41 at 1:1 ratio and treated with cycloheximide for the indicated periods of time. (e) Quantification of RNF43 in WB of (d) normalized over GAPDH. (f) Anti-HA WB of STF-RZ-DKO, DLD, and LoVo cells transfected with increasing amounts of DNA of HA-tagged RNF43-WT and G659Vfs*41 plasmids pre-mixed at 1:1 ratio. GAPDH and actin were loading controls.