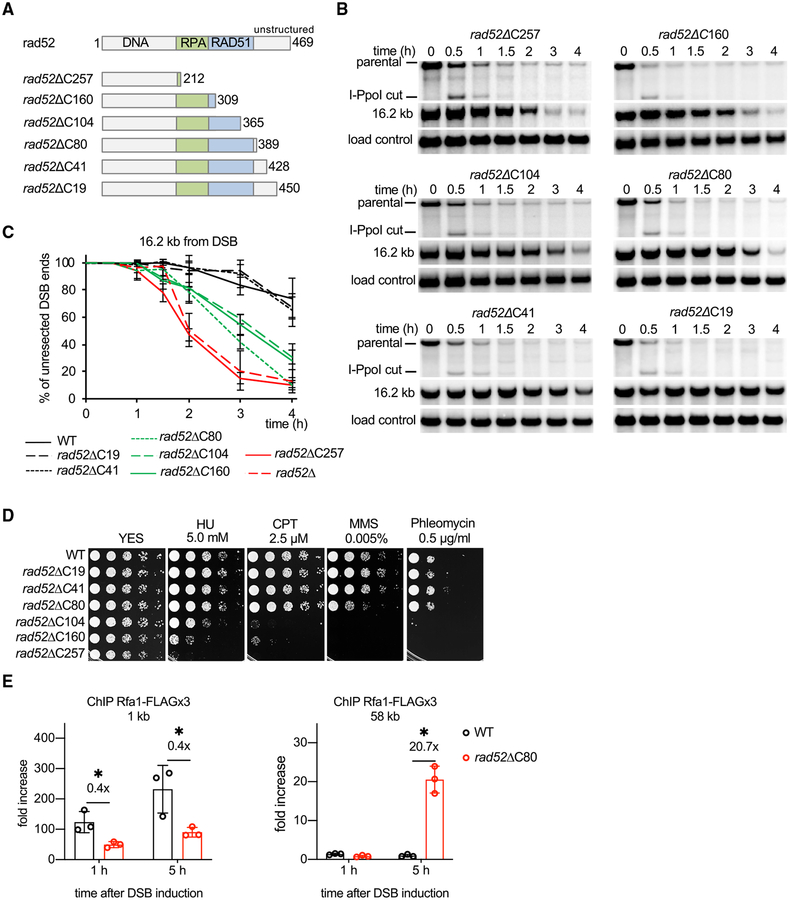
Figure 3. Role of the C-Terminal Region of Rad52 in Extensive Resection.
(A) Schematic showing major Rad52 domains and truncation mutants analyzed.
(B) Southern blot analysis of resection in indicated rad52 truncation mutants.
(C) Plots showing kinetics of resection in rad52 mutants. Error bars denote SD (n = 3).
(D) Analysis of sensitivity to DNA damage of wild-type and rad52 mutant strains. 5-fold serial dilutions were made, and 2 μL was spotted onto yeast extract with supplements (YES) or YES with hydroxyurea (HU), camptothecin (CPT), methyl methanesulfonate (MMS), or phleomycin.
(E) ChIP-qPCR analysis of recruitment of RPA (Rfa1 subunit, called Ssb1 in fission yeast) in wild-type and rad52ΔC80 cells at 1 and 58 kb from the DSB end at lys1 locus. Error bars denote SD (n = 3). One-tailed p values were shown (*p < 0.05).