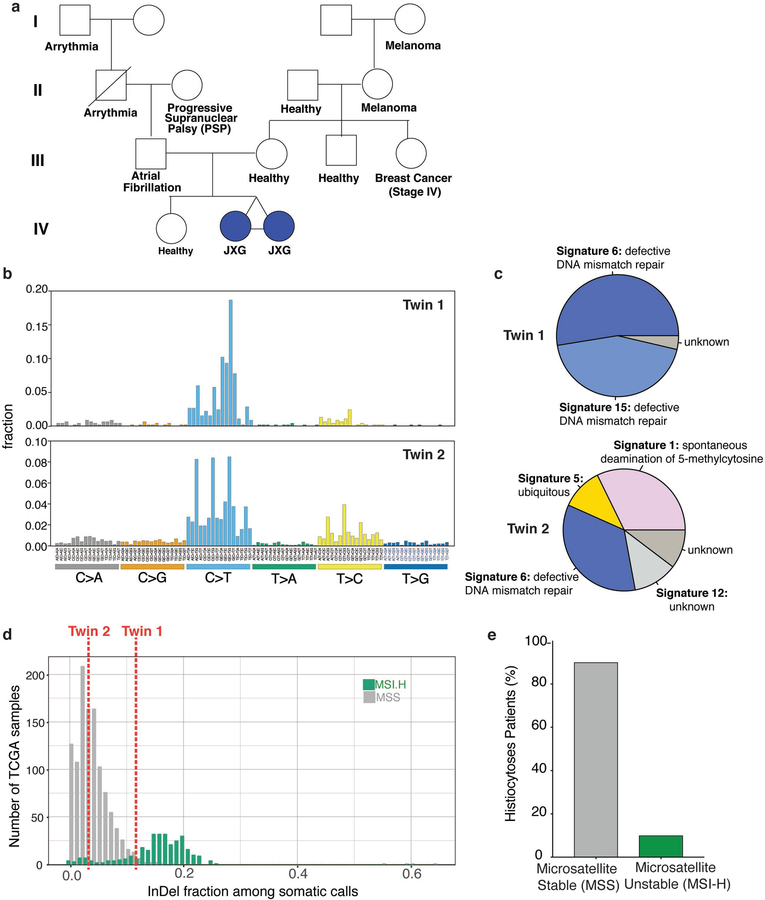
Extended Data Fig. 1. Pedigree and genomic analyses of monozygotic twins with CSF-1R mutant Juvenile Xanthogranuloma (JXG).
(a) Pedigree of twins with JXG. Twin 1 and 2 are monochorionic, diamniotic identical twins born to an otherwise healthy 35-year-old mother. At one year of age, both twins developed small skin lesions on their forehead, which over the course of four months grew in number and diameter extending to the scalp and upper chest. Scalp biopsies were consistent with a diagnosis of JXG. Ophthalmic examination of both twins also identified multiple, bilateral subconjunctival lesions compatible with JXG in twin 1 only. Both twins were monitored in our institution until 2.5 years-of-age with stable, persistent JXG with no visual compromise or neurologic signs or symptoms, and therefore no indication for therapy. Complete blood counts and comprehensive metabolic profiles of both twins have been within normal limits since birth. (b) Mutational profile of the JXG lesion from each twin displaying the fraction of mutations found in each trinucleotide context (performed using deconstructSigs26). (c) Piechart showing the relative contribution of each mutational signature in the JXG lesion from (b) in each twin (based on the 30 mutational signatures detected by Sanger/COSMIC30). Signatures 6 and 15 are associated with defective DNA mismatch repair. (d) Histogram illustrating the fraction of indels among all mutations identified in the JXG lesions of twins 1 and 2 (red dashed lines) along with the distribution of indel fractions for TCGA samples (colorectal, endometrial, ovarian, stomach) with known microsatellite instability (MSI) status assayed from mononucleotide markers (as described previously29; MSI-H: high microsatellite instability; MSS: microsatellite stable). (e) Bar graph depicting proportion of histiocytosis samples that are MSS (90%; n=28/31) versus MSI-H (10%; n=3/31) based on WES.