Figure 2.
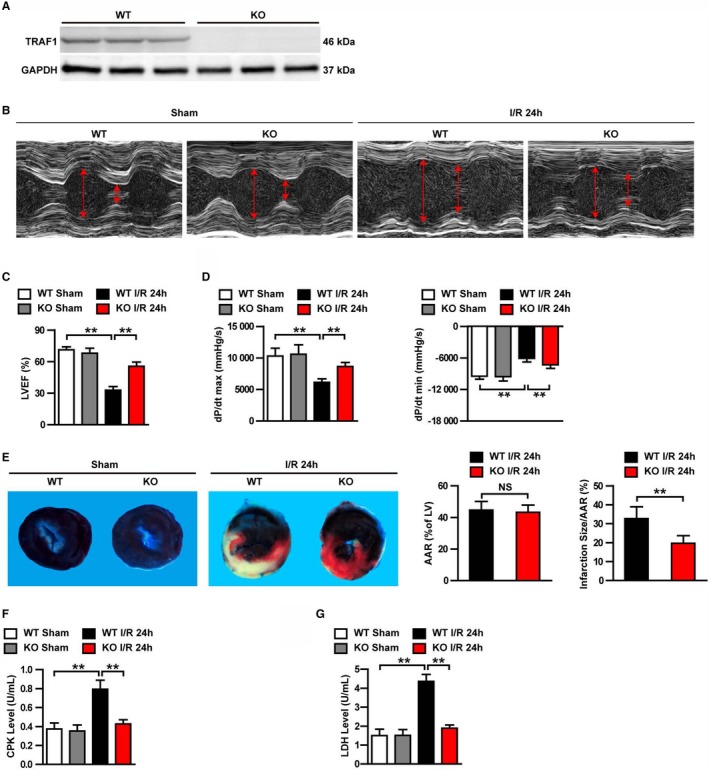
TRAF1 deficiency protected mouse hearts against I/R injury. A, Western blot of TRAF1 expression in KO and WT mice (n=3 per group). GAPDH served as loading control. B, Representative images of echocardiography in WT and TRAF1‐KO mice before (sham) and 24 hours after I/R. C and D, Echocardiographic (C) and hemodynamic (D) assessment of cardiac function in sham and I/R mice (n=10 per group). E, Images of myocardial tissues (Evans blue combination with TTC staining) from WT and TRAF1‐KO mice before (sham) and 24 hours after I/R. The ratios of AAR to left ventricle and infarction size to AAR were quantified by Image‐Pro Plus 6.0 (Media Cybernetics) in the WT and KO groups (n=5 per group). F and G, Quantitative results of serum CKP (F) and LDH (G) before (sham) and 24 hours after I/R (n=10 per group). For statistical analysis, 1‐way ANOVA was used for panels B, D, F, and G; a 2‐tailed Student t test was used for panel (E). **P<0.01. Red arrows represent the left ventricular end‐diastolic and end‐systolic dimension. AAR indicates area at risk; CPK, creatine phosphokinase; dP/dt max, decreased maximum rate of pressure increase; dP/dt min, decreased minimum rate of pressure increase; I/R, ischemia/reperfusion; KO, knockout; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; LV, left ventricle; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; NS, not significant; TRAF1, tumor necrosis factor receptor–associated factor 1; WT, wild type.
