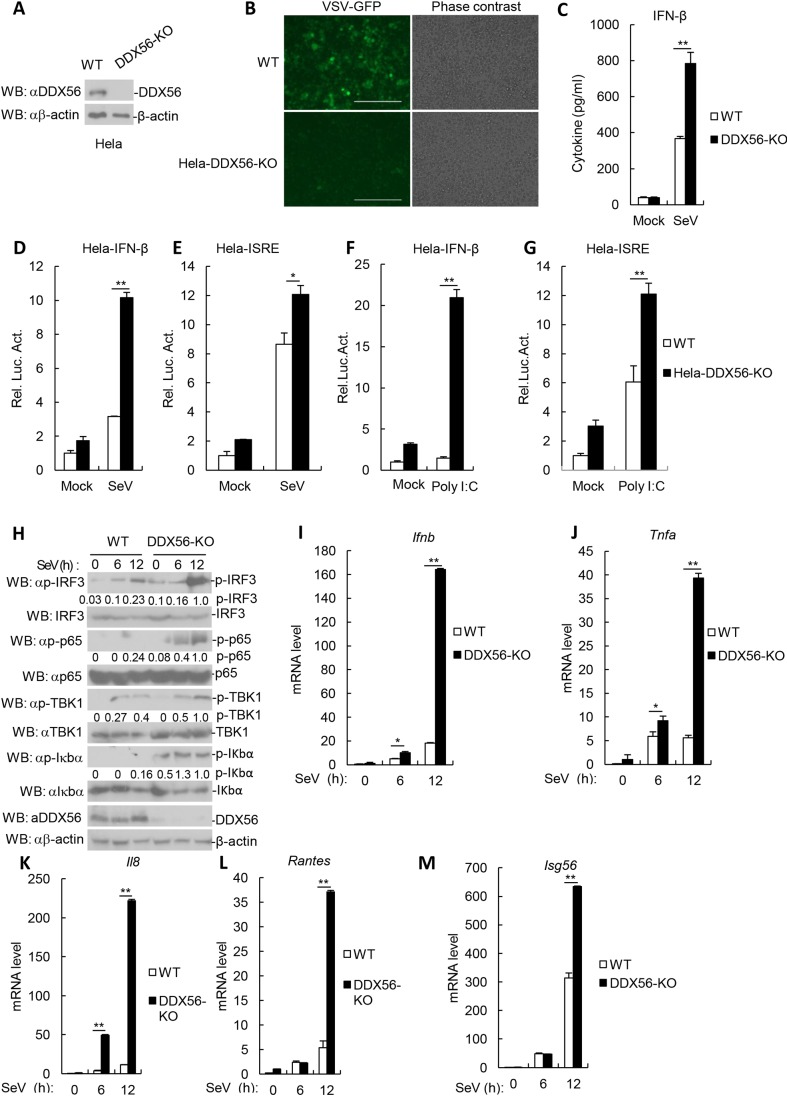
Fig. 3.
Knockout of DDX56 potentiates RNA virus-triggered IFN-β signaling. (A) DDX56 levels in the HeLa cells were analyzed by immunoblotting. (B) VSV replication in wild-type and DDX56- knockout (KO) HeLa cells. HeLa (5×104) were infected by VSV–GFP (MOI 0.1) for 2 h and imaged by microscopy. Scale bar: 400 µm. (C) Effects of DDX56 deficiency on secretion of IFN-β induced by SeV in HeLa cells. DDX56-knockout HeLa cells were infected with SeV for 12 h. The culture medium was collected for quantification of the indicated cytokines by ELISA. The experiment shown is representative of three independent experiments with mean±s.d. of three technical replicates. **P<0.01. (D–G) Effects of DDX56 knockout on SeV- or poly(I:C)-induced activation of the IFN-β promoter and ISRE. DDX56-knockout HeLa cells (105) were transfected with the IFN-β promoter or ISRE (100 ng). At 24 h after transfection, the cells were left uninfected or infected with SeV for 12 h or were treated or untreated with poly(I:C) (1 µg/ml) for 18 h before reporter assays were performed. Shown are representative experiments of three independent experiments with mean±s.d. of three technical replicates. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. (H) Effects of DDX56 deficiency on SeV-induced phosphorylation of TBK1, IRF3, p65 and IκBα. The DDX56-knockout HeLa cells were untreated or treated with SeV for the indicated times, and cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. The degree of protein phosphorylation was calculated by ImageJ software and is presented under the blot. (I–M) Effects of DDX56 deficiency on SeV-triggered transcription of IFNB1 and TNFa genes. The DDX56-knockout HeLa cells (4×105) were left uninfected or infected with SeV for 12 h before qRT-PCR was performed. Shown are representative experiments of three independent experiments with mean±s.d. of three technical replicates. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. WT, wild type; Luc, luciferase.