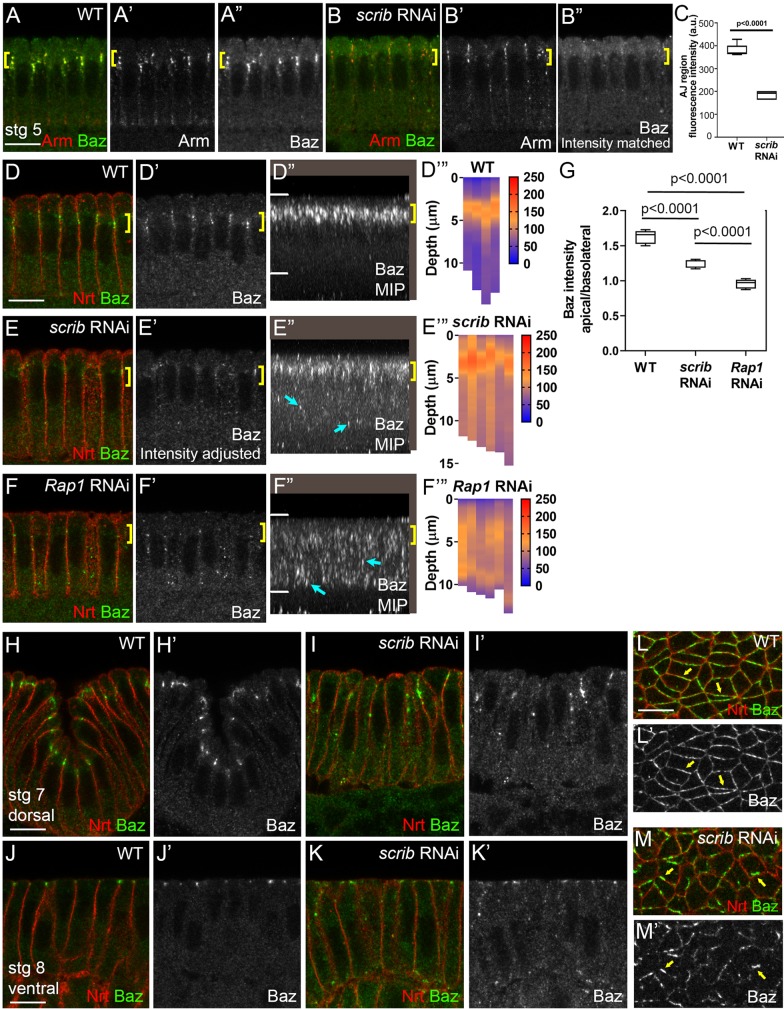
Fig. 5.
Scrib is required for Baz cortical retention and apical clustering. (A-B″) Intensity matched images showing Arm and Baz in scrib-RNAi versus wild type. scrib-RNAi impairs Baz cortical retention during cellularization (yellow brackets). (C) Quantification of cortical Baz (data are median, upper and lower quartile limits, and range). (D,D′,E,E′,F,F′) Intensity-adjusted images, Baz during cellularization. (D″,E″,F″) MIPs. Apical Baz retention (yellow brackets) is reduced after scrib-RNAi (E), with ectopic puncta observed basolaterally (E″, cyan arrows) – this is distinct from the complete loss of Baz apical retention after Rap1-RNAi (F″). (D‴,E‴,F‴,G) Quantification of pixel intensities along the apical-basal axis. (G) Box and whisker plots; data are median, upper and lower quartile limits, and range. (H-K′) After gastrulation onset, Baz is lost from AJs and displaced as small puncta along the apical-basal axis in scrib-RNAi. (L-M′) En face sections through AJs at stage 7. Baz circumferential distribution becomes more irregular (yellow arrows). Scale bars: 10 µm.